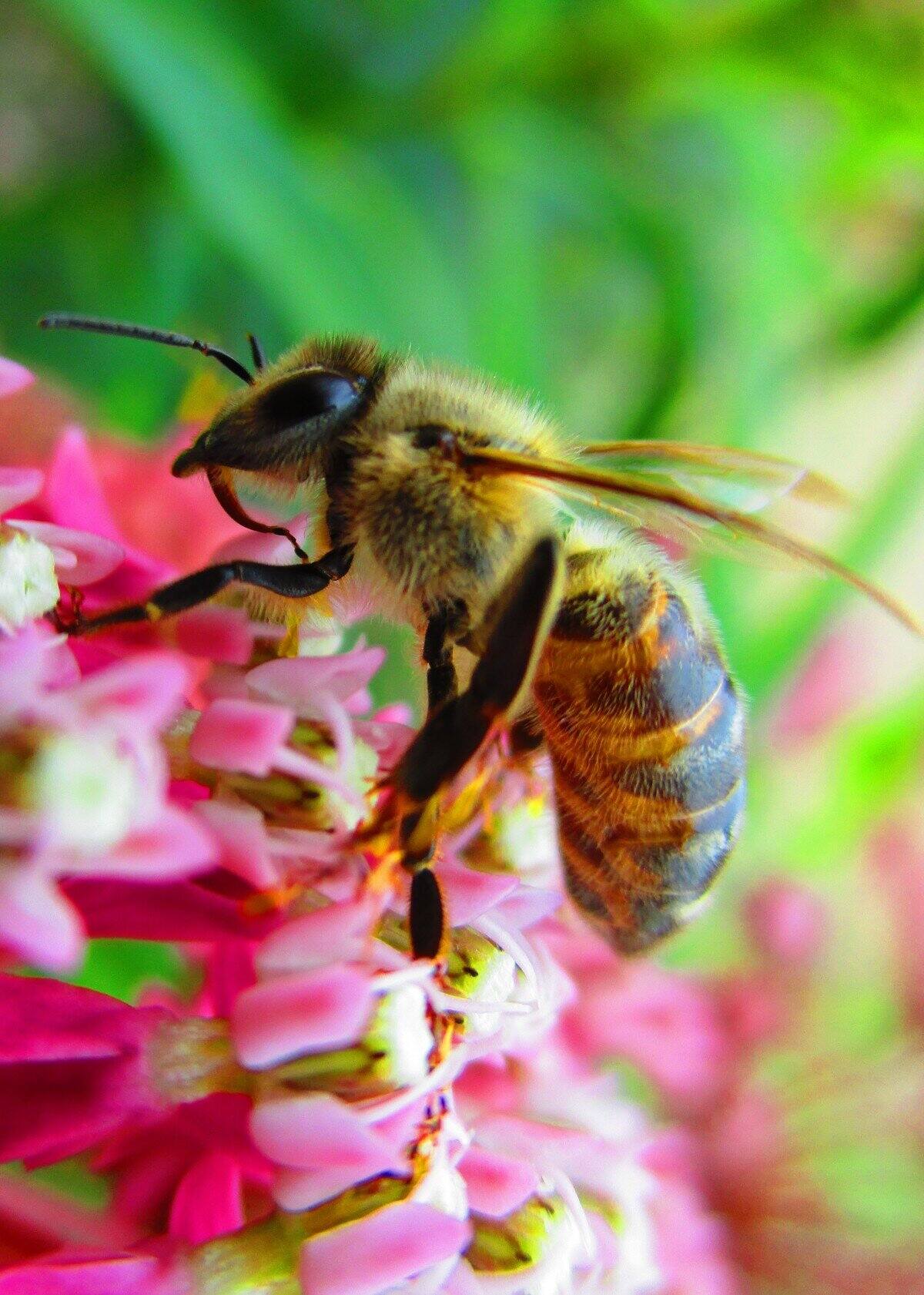
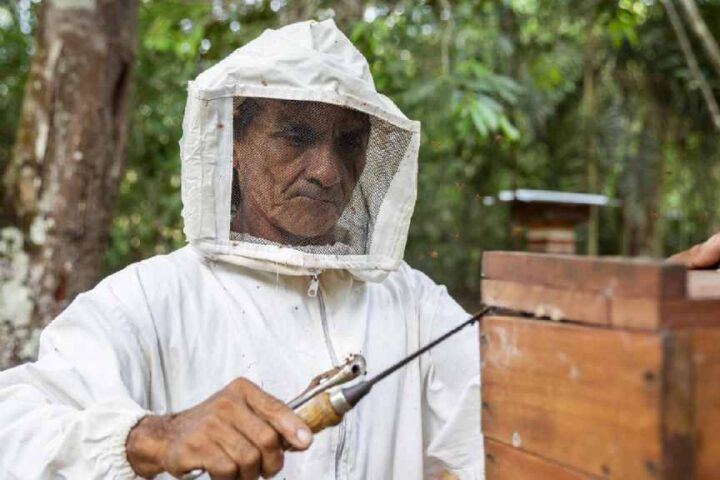
The planet joins the celebration and conservation of bees on World Bee Day, commemorated every May 20th. Many raise awareness that higher levels of the trophic chain depend directly on the successful pollination of plant species carried out by bees among other species, both wild flora and cultivated species.
The activities carried out by honey bees affects both wildlife and species used in animal production, such as livestock. Therefore, the function of pollination ultimately depends on human nutrition and food security. All the efforts of scientists are aimed at finding solutions to mitigate the decline in bee populations since the 1990s.
This year, World Bee Day focuses on the theme “Engagement with Bees, Hand in Hand with Youth,” highlighting the importance of involving young people in beekeeping and pollinator conservation efforts, as they are the guardians of our environment.
Global agricultural expansion has led to a significant loss of habitat for bees, exacerbated by the use of pesticides that harm their essential flora. Climate change, with rising temperatures, has caused the death of many colonies and displaced others from their usual zones.
The ongoing decline in bee populations is a global concern. However, there is good news from the United States. According to official reports, they are recording record numbers in honey bee populations. It seems they have found a formula for recovery. Yet, the figures puzzle experts who insist that the danger persists.
Similar Post
The introduction of foreign species for the pollination of specific crops has brought pathogens that trigger pandemics in these populations. Despite their crucial role as pollinators for most of our planet’s species and crops, studies indicate a downward trend in bee diversity worldwide, raising concerns about the future of these essential pollinators.
Of the 20,000 existing bee species, many are responsible for pollinating 85% of global crops and fruits. However, in recent decades, the number documented in the wild has decreased worldwide: a quarter of the species have not been observed since the 1990s.
Protecting bees is essential to maintaining healthy ecosystems and ensuring the pollination of wild and cultivated plants. Each of us can contribute to their conservation:
- Avoid using toxic phytosanitary products, especially during flowering, so that bees are not poisoned during pollination or carry toxins back to the larvae they feed in the hive.
- Planting melliferous species in your garden to provide food that can improve their health.
- Calling emergency teams to remove Asian hornet nests, as this invasive and very aggressive species preys on honey bees.
- Buying honey from local producers and supporting beekeepers who care for the health of bees.
- Rescuing hives if you find one in a location that interferes with the use of that space.
Fortunately, some farmers have finally begun taking measures because they have realized the valuable services that bees provide and how their scarcity is directly related to the decline in crop production, he highlighted.
The latest U.S. Agricultural Census reveals unprecedented growth in honey bee populations. Nearly a million colonies have been added in the last five years, reaching a total of 3.8 million. Since 2007, honey bees have been the fastest-growing livestock segment in the country, not counting wild bees, which outnumber domesticated ones.