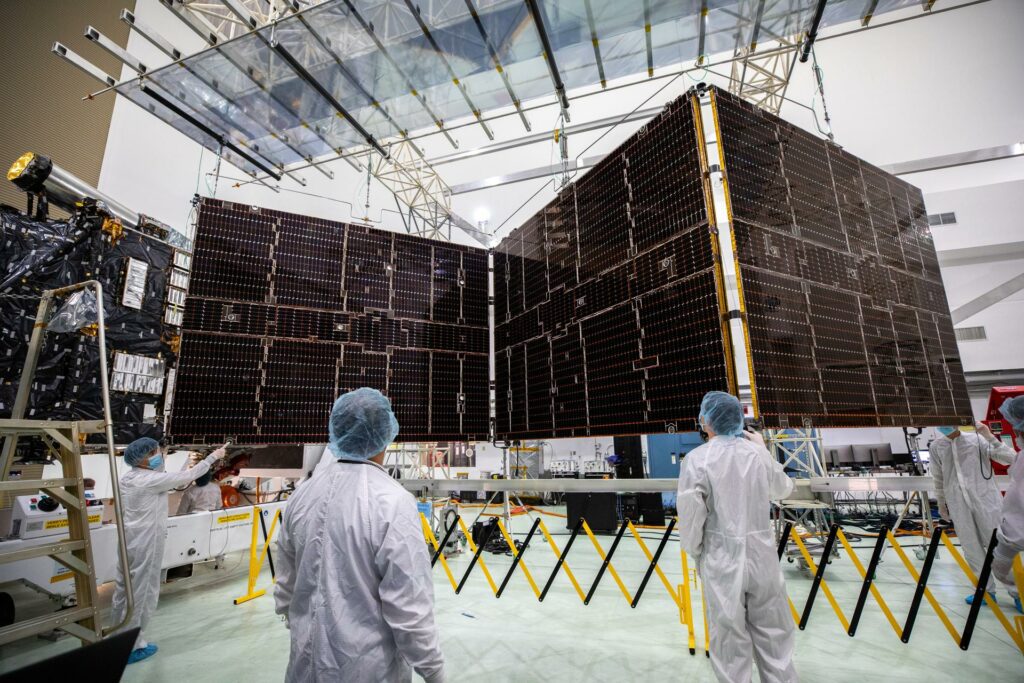
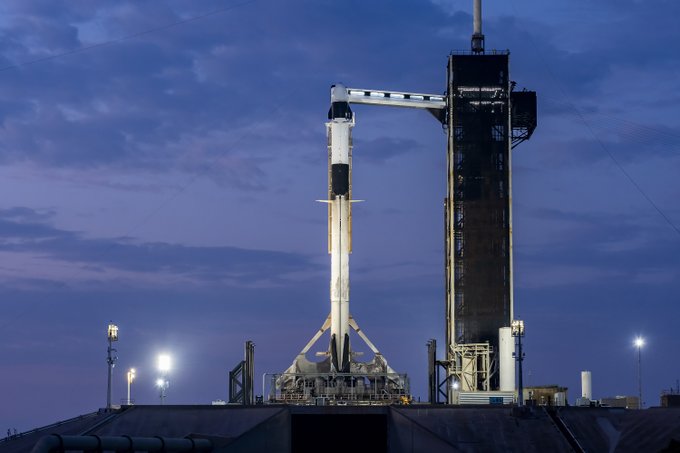
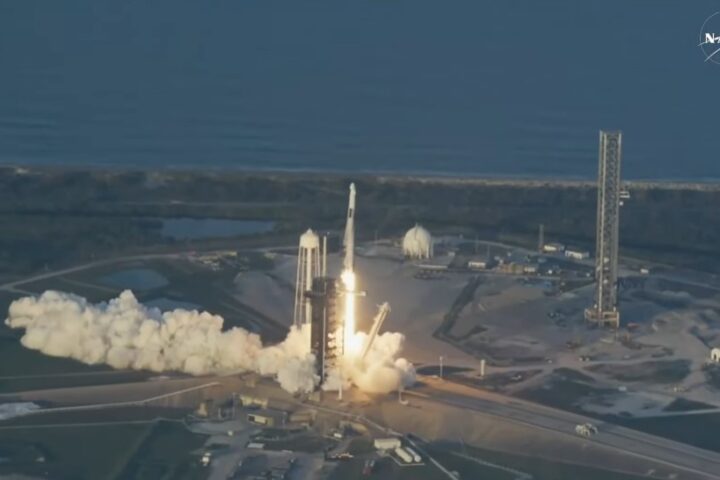
NASA’s Psyche spacecraft is on track for its monumental journey, with its launch date set for October 5th. The spacecraft’s colossal solar arrays, vital for its 2.5 billion-mile voyage to a metal-rich asteroid, have been meticulously tested and permanently affixed. This significant installation occurred at the Astrotech Space Operations facility, in proximity to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. “The solar arrays’ successful installation marks a pivotal step towards ensuring the spacecraft’s operational efficiency throughout its expedition,” remarked Tony Greicius, a seasoned writer at NASA. Once the spacecraft departs Earth, these solar arrays will remain securely stowed until they reach their destination in July 2029.
The primary objective of the Psyche mission is to orbit the asteroid, capturing images and collecting data for a span of 26 months. Scientists are optimistic that this mission will provide insights into the asteroid’s composition, potentially revealing details about planetary cores and Earth’s genesis. These solar arrays, spanning an impressive 800 square feet, are the largest ever to be deployed at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Despite their vast size, these arrays will generate just over 2 kilowatts of power when the spacecraft is near the asteroid, given its distance from the Sun. This power is sufficient to cater to Psyche’s electrical demands, including operating scientific instruments and the spacecraft’s highly efficient solar electric propulsion engines.
Concurrently, NASA is pioneering advancements in deep space communication through its Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) project. This project aims to leverage lasers to enhance data transmission speeds, surpassing the capabilities of existing radio frequency systems. “DSOC’s potential to amplify data-return capacities by up to a hundredfold represents a monumental leap in space communication technology,” stated Abi Biswas, DSOC’s project technologist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The DSOC’s innovative near-infrared laser transceiver will be an integral component of the Psyche mission, facilitating communication with ground stations in Southern California. Naomi Hartono, an editor at NASA, emphasized the significance of laser communication, highlighting its potential to transmit more intricate scientific data, even enabling video streaming from Mars.
Similar Posts
The DSOC transceiver boasts groundbreaking technologies, including a photon-counting camera and an 8.6-inch telescope, designed to lock onto high-power near-infrared laser uplinks. “The challenges posed by the vast distances in deep space communication are immense, but DSOC is equipped to overcome them,” remarked JPL’s Bill Klipstein, the DSOC project manager. The DSOC will operate for nearly two years post the Psyche mission’s launch, culminating in its Mars flyby in 2026. It’s worth noting that while DSOC will be hosted by the Psyche spacecraft, it will not relay Psyche mission data, ensuring the independent evaluation of both projects.
DSOC is a testament to NASA’s commitment to fostering cutting-edge communication technologies, setting the stage for future space missions. “DSOC’s advancements are not just about speed but about ensuring consistent, high-quality data transmission, even from the remotest regions of our solar system,” commented Trudy Kortes, director of the Technology Demonstrations Missions program at NASA Headquarters. The Psyche mission, spearheaded by Arizona State University, is a part of NASA’s illustrious Discovery Program. JPL, a division of Caltech, is entrusted with the mission’s comprehensive management, from system engineering to mission operations. As the countdown to the Psyche mission’s launch commences, the global scientific community awaits with bated breath, eager to witness the next chapter in space exploration. The future of space exploration and communication is on the cusp of transformation, with projects like Psyche and DSOC leading the charge. As we venture deeper into the cosmos, these endeavors underscore the boundless potential of human ingenuity and our relentless quest for knowledge.