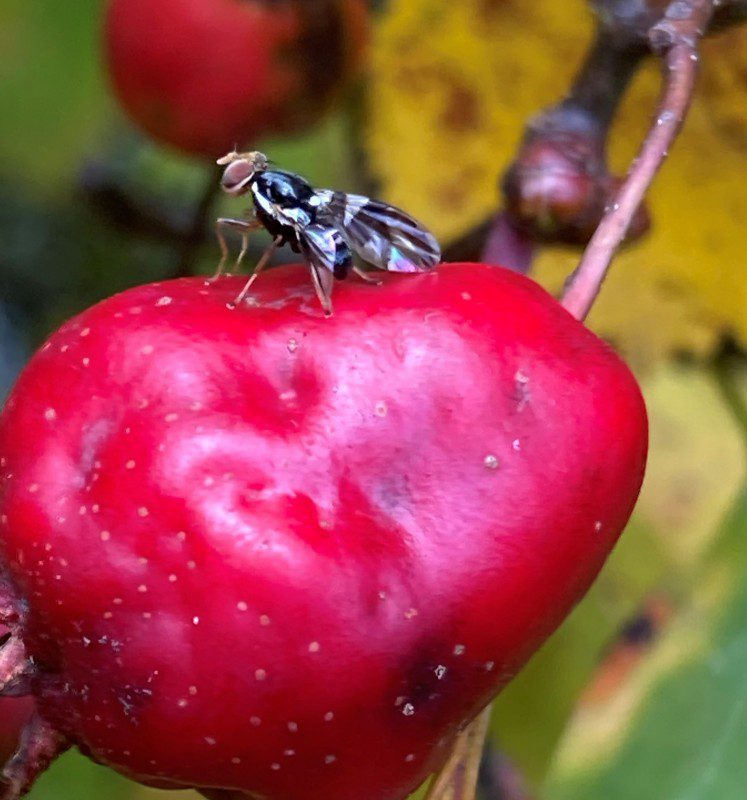
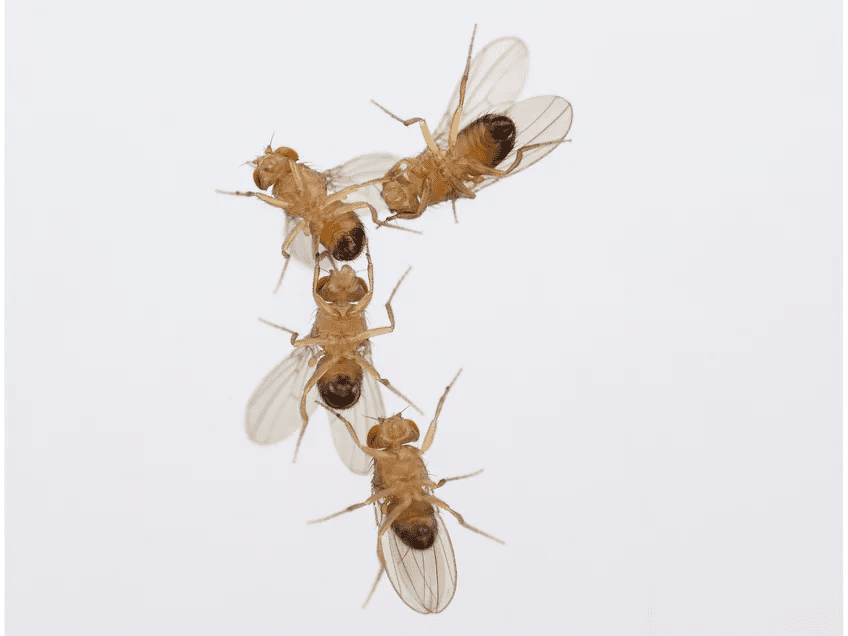
Thomas H.Q. Powell and his team conducted a study that primarily focused on the impact of changing temperatures on two diverging populations of the Hawthorn fly. While one population continued to feed on the hawthorn fruit, the other resorted to consuming apple trees in the 1850s. An investigation was conducted to determine how future temperature changes may affect these populations and how they interact with parasitic wasps. The hawthorn-eating flies were resilient to shifts in temperature. This may have taken place because of greater genetic variation. The apple-eating flies were thrown out of sync with the trees, and the future temperature scenario seemed to disrupt their life cycles.
There could be a loss of synchronization with other species because of this mismatch. This also includes the parasitic wasps that prey on them. The study brings to light how vulnerable species interactions remain and the disruptions that climate change can cause. Powell stresses the importance of parasitoid wasps. These creatures play a crucial role in controlling populations of insects that feed on plants. This also includes agricultural pests. Although insects experience climate change in many ways, some suffer more than others. Some species face challenges like land-use change, habitat loss, and fragmentation. This is due to ecological specializations that cause stress and delay adaptation in a world that is constantly changing.
Similar Post
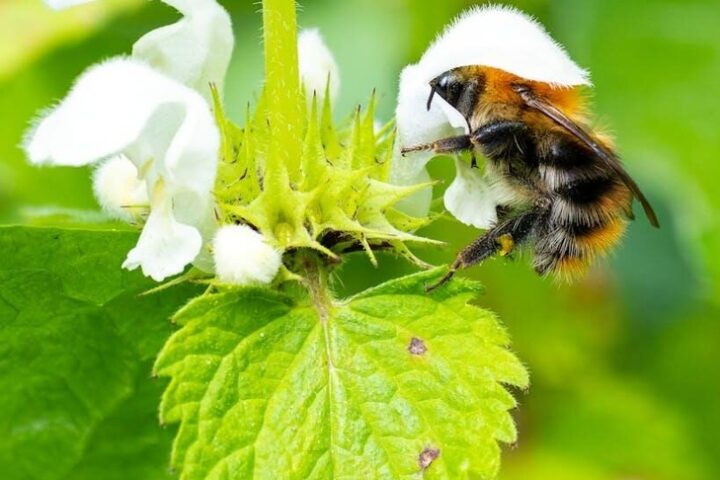
Alycia C.R. Lackey, a co-author of the paper, mentioned that there are certain species that may benefit from warmer temperatures, such as those with wider temperature tolerances or those able to withstand higher temperatures. However, the same does not stand for many pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and moths. These insects are crucial for crop pollination and are severely threatened by temperature rises. Additionally, some crop pests may thrive under warmer climate conditions, further jeopardizing agricultural yields.
Limiting the progression of climate change to mitigate its impacts on insects is essential. The importance of preserving intact habitats and maintaining connectivity between them should be emphasized. This is necessary to allow ongoing evolutionary processes to recover and bear the burden that comes with the stresses posed by climate change. Conservation efforts, such as the 30×30 initiative to protect 30 percent of the world’s land and ocean area by 2030, are crucial steps in addressing these challenges.