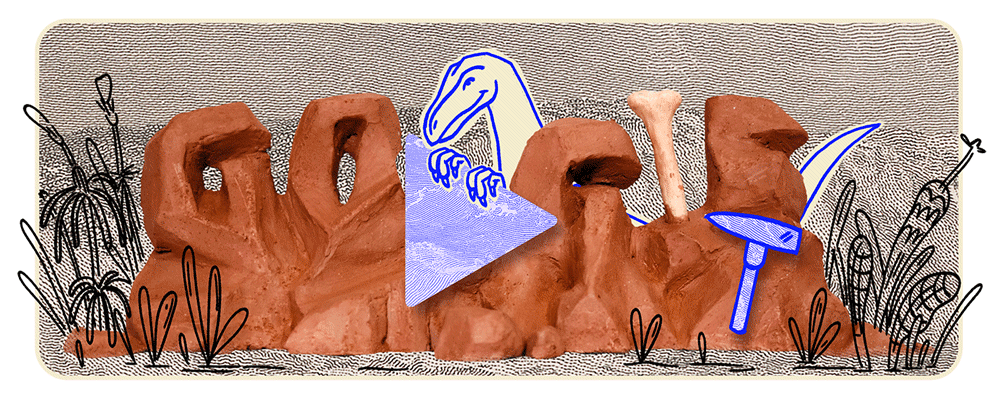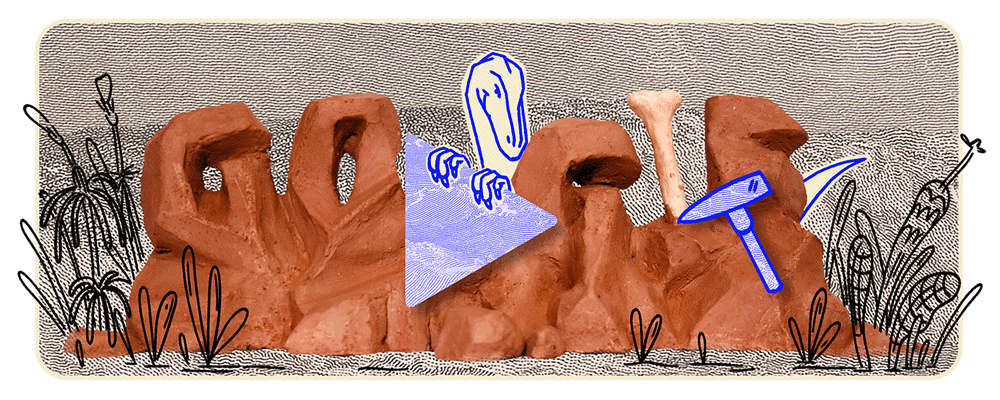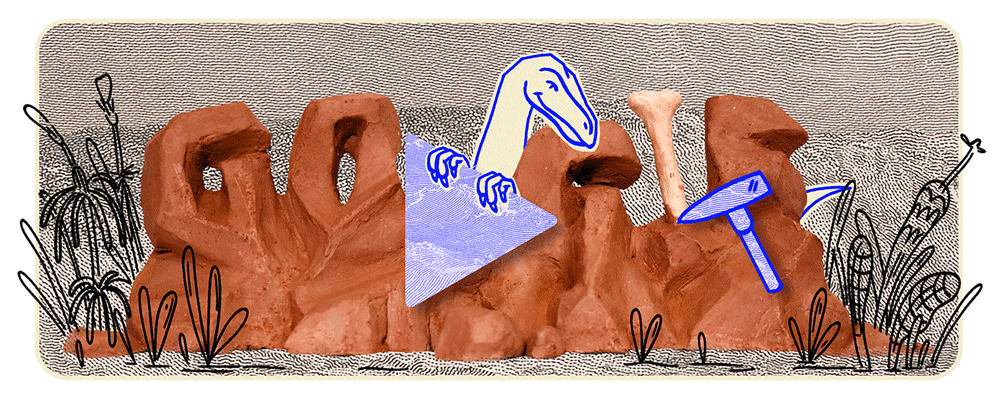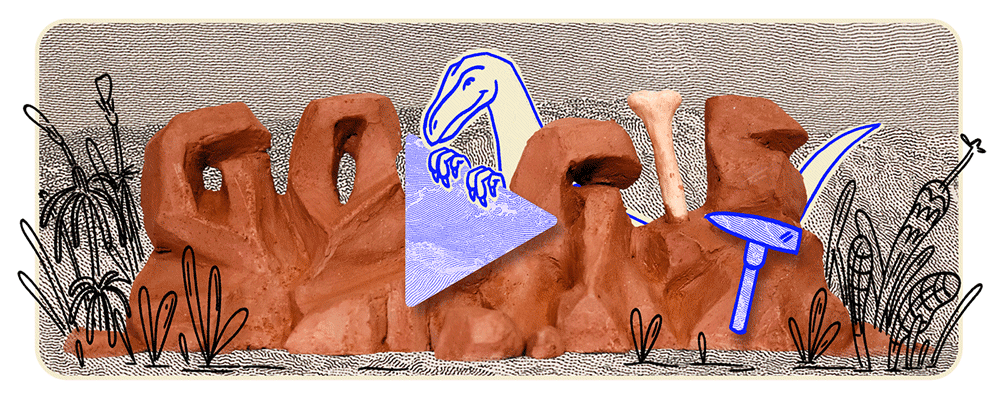
On October 19, 2024, Google’s homepage featured an animated Doodle celebrating Staurikosaurus, an early theropod dinosaur discovered in Brazil in 1936. This tribute marks the anniversary of the 2010 silhouette reconstruction by paleontologists Oscar Alcober and Ricardo Martinez, which reignited interest in the species. The Doodle depicts Staurikosaurus sprinting across a prehistoric landscape, showcasing its distinctive features, recreated through fossil impressions arranged on clay and brought to life using stop-motion recording techniques. This engaging digital homage highlights the enduring fascination with one of Earth’s earliest predators and the meticulous artistry behind Google’s commemorative animations.
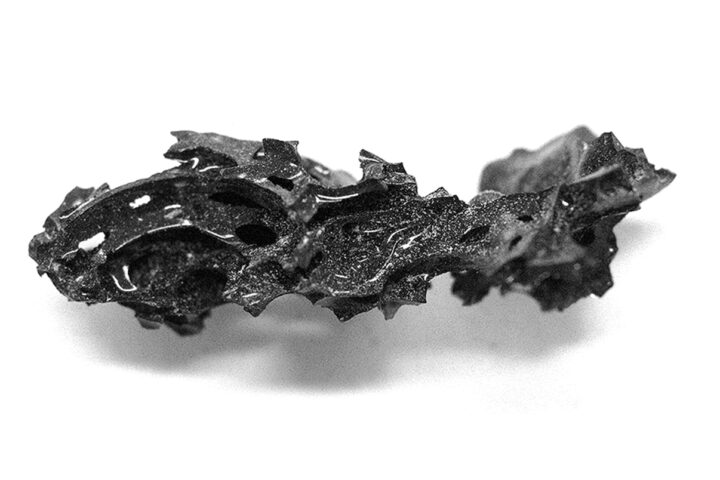
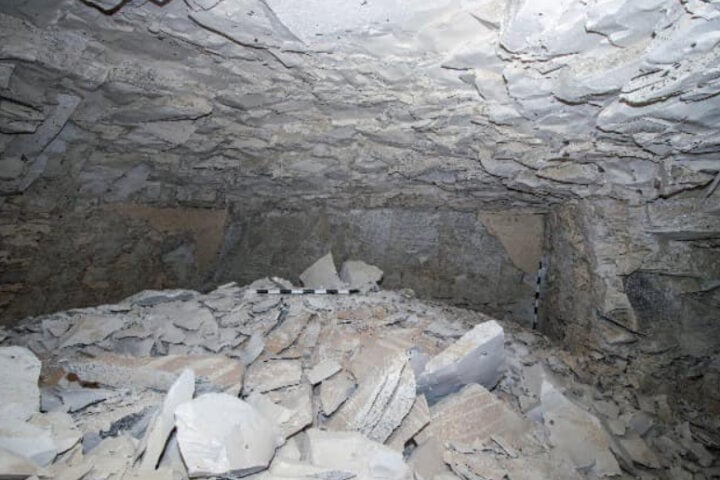
Paleontologist Llewellyn Ivor Prince unearthed the Staurikosaurus fossil at the Santa Maria Formation in southern Brazil. While often referred to as “radiocarbon dated,” the fossil’s age was actually determined using other radiometric dating methods appropriate for its Triassic origins. These techniques placed the Staurikosaurus at approximately 225 million years old, situating it in the late Triassic period.
In 1936, Dr. Llewellyn Ivor Price highlighted how the discovery of Staurikosaurus significantly advanced our comprehension of dinosaur evolution.
The Staurikosaurus, which translates to “Southern Cross Lizard” after its celestial origin, provides a rare glimpse into early dinosaur evolution. Standing about 80 cm tall and measuring 2 meters long, this bipedal predator weighed an estimated 30 kg.
Key features of the Staurikosaurus include:
- Bipedal stance with a long tail for balance
- Sharp, curved, serrated teeth adapted for carnivorous feeding
- Agile body structure indicating swift movement
These adaptations suggest the Staurikosaurus was an efficient predator, likely targeting smaller reptiles and early mammals of its time. Comparing Staurikosaurus to later theropods like Megalosaurus reveals the evolutionary trajectory of this dinosaur group. While sharing basic theropod characteristics, Staurikosaurus exhibits more primitive features, reflecting its earlier position in the evolutionary timeline.
Similar Posts
Because Staurikosaurus lived during the Late Triassic period, around 225 million years ago, studying such early dinosaurs helps scientists piece together how dinosaurs evolved from their ancestors. Its physical characteristics, like bipedal stance and sharp teeth, offer insights into the adaptations that allowed dinosaurs to thrive and diversify.
The Staurikosaurus finding continues to influence modern paleontological research. Its unique position in dinosaur evolutionary history provides valuable data for understanding the emergence and diversification of theropods.
The Google Doodle serves as a digital portal to paleontology and early dinosaur evolution. As research progresses, Staurikosaurus remains a key piece in the complex puzzle of prehistoric life, driving both scientific inquiry and public fascination with Earth’s ancient past.
Numerous resources exist for those intrigued by this glimpse into prehistoric life to explore dinosaur evolution further. Natural history museums worldwide often feature exhibits on early dinosaurs, while online platforms provide access to the latest paleontological research and discoveries.