The renewable energy landscape in South Africa has taken a significant step forward with the grid connection of the 100-megawatt Redstone Concentrated Solar Thermal Power (CSP) Plant. Constructed by Power Construction Corporation of China (PowerChina), this facility marks a series of firsts for the region and represents a substantial investment in clean energy technology.
Project Overview and Technical Specifications
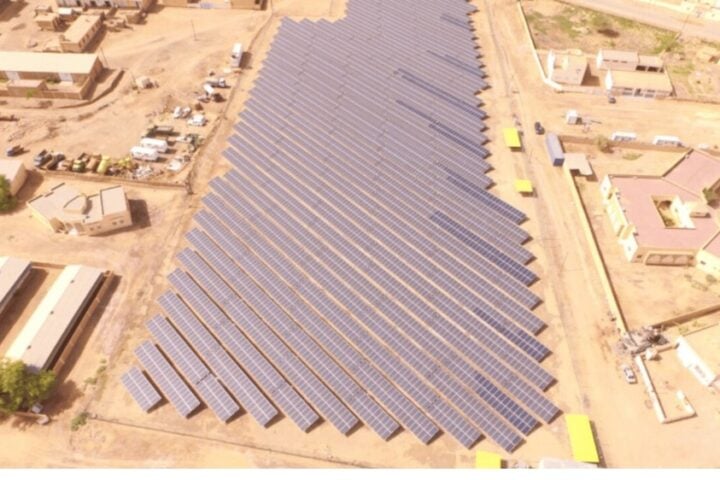
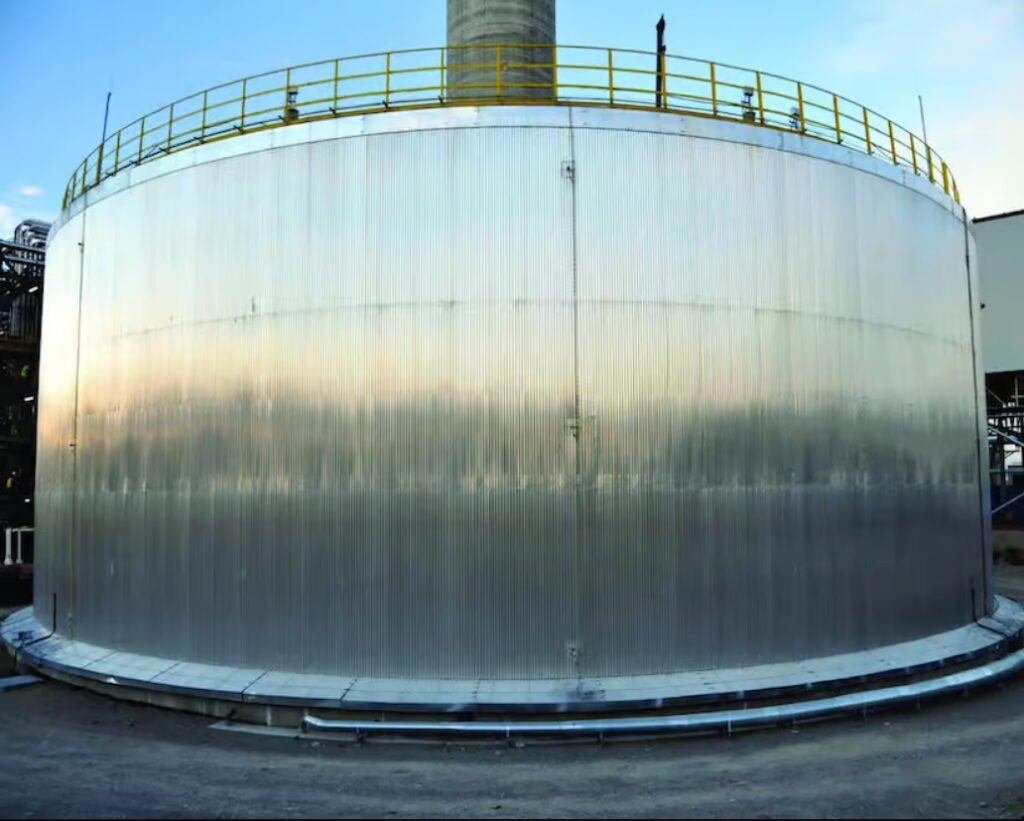
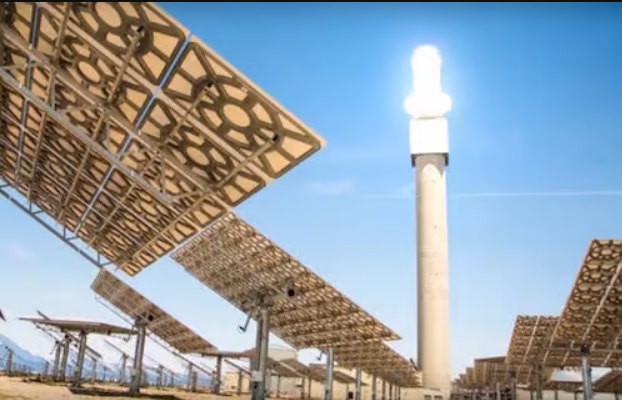
Located in the Siyanda district of Northern Cape, the Redstone CSP plant is the first tower-based molten salt CSP plant south of the Sahara Desert. The facility boasts an impressive array of 41,260 heliostats, which direct sunlight onto the solar tower’s heat receiver. This advanced system heats molten salt from approximately 260°C to 565°C, storing the thermal energy for later use.
One of the plant’s key features is its ability to provide up to 12 hours of full-load electricity generation, ensuring a stable power supply even after sunset. This capability addresses one of the primary challenges of solar energy: intermittency.

Economic and Environmental Expectations
The Redstone CSP plant is set to deliver 480 gigawatt-hours of clean electricity annually to South Africa’s power grid, meeting the energy needs of around 200,000 households. This output will be supplied to Eskom, the state-owned utility, under a 20-year power purchase agreement (PPA).
From an economic perspective, the project has already made a substantial impact. During peak construction, it employed approximately 1,800 workers, generating over 600 local jobs. As the largest investment project in the Northern Cape Province, with a total investment of $724 million, it has injected significant resources into the local economy.
Similar Posts
Stakeholders and Funding
Saudi Arabia’s ACWA Power holds a 49% stake in the facility, making it the largest shareholder. The project was selected as part of South Africa’s Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Procurement (REIPP) program, reflecting the country’s commitment to diversifying its energy mix.

Environmental Benefits and Future Prospects
The Redstone CSP plant is expected to play a crucial role in reducing South Africa’s reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions. This aligns with the country’s renewable energy targets and international climate commitments.
As the first of its kind in sub-Saharan Africa, the Redstone CSP plant serves as a proof of concept for similar projects in the region. Its success could pave the way for further investments in concentrated solar power and other renewable energy technologies, contributing to a more sustainable energy landscape in South Africa and beyond.

Technical Challenges and Innovations
The integration of the molten salt storage system presented significant engineering challenges. The successful implementation of this technology marks a major achievement in the field of concentrated solar power, potentially influencing future projects globally.

Expert Opinions
Paddy Padmanathan, President & CEO of ACWA Power, remarked, “ACWA Power is proud to lead the energy transition in countries that are committed to ambitious renewable energy targets to support economic growth and social development. Redstone CSP adds another superlative to our budding record in South Africa, being the largest renewable energy investment to date. As grid links are improved, the ingenuity of the private sector together with the great support of experienced finance partners has the potential to spark lasting impact for local communities and address the threats of climate change.”
“Understanding that South Africa is on a just transition in terms of investing a lot in energy,” explained Mthoko Ngidi, project manager of its South African partner. ”China, being a world leader in terms of building renewable energy, is sitting in a very advantageous position in terms of participating,” he added.

The Solar Future
The Redstone CSP plant represents a major milestone in South Africa’s journey towards a more sustainable energy future. Its successful grid connection and innovative technology showcase the potential for large-scale renewable energy projects to meet growing power demands while reducing environmental impact. As the project moves forward, it will be crucial to monitor its performance and impact on both the local economy and the broader energy sector.