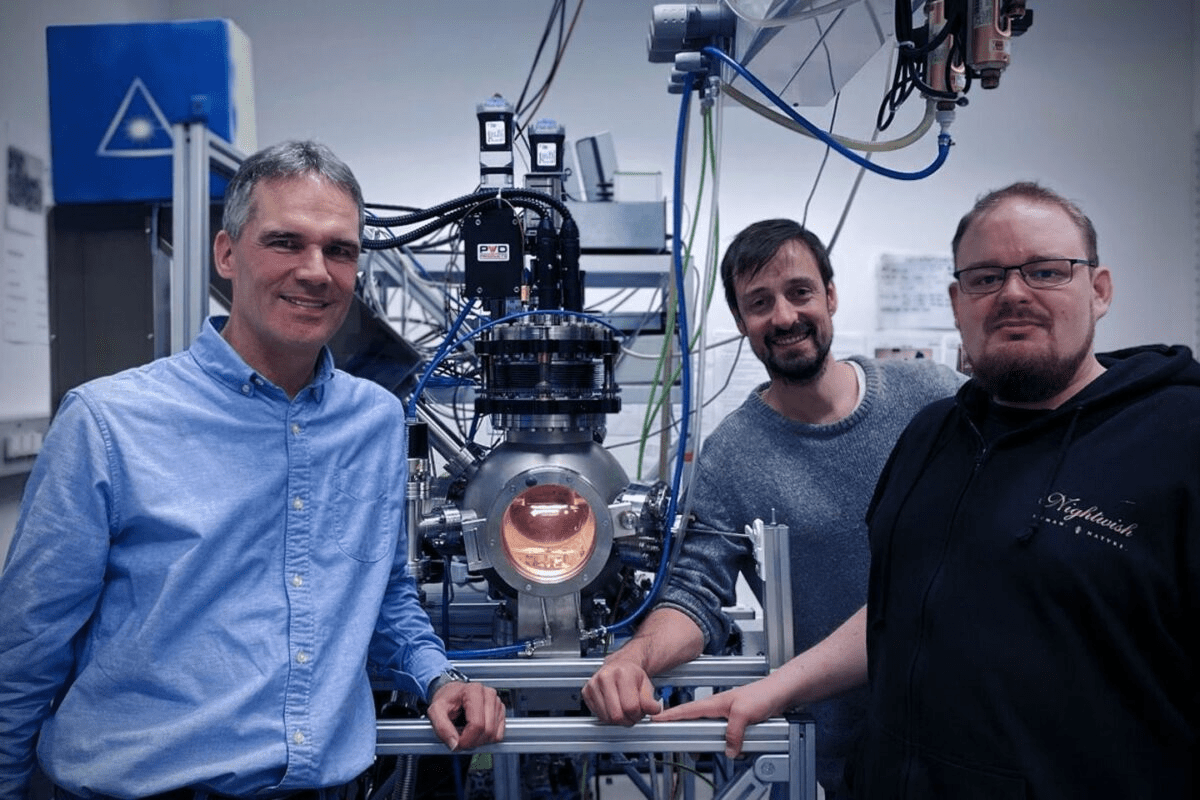
The Vienna University of Technology (TU Wien) has made a new breakthrough in the form of regenerative oxygen-ion batteries, which have the potential to replace lithium-ion batteries in various key applications.
Challenges with Lithium-Ion Batteries
The nervy storage device like the lithium-ion batteries suffers from several issues, including overheating that can lead to fires and a decline in effectiveness over time. A significant amount of water is required for the production of lithium batteries, with one ton of lithium obtained through mining requiring 2.2 million gallons of water, causing adverse effects on communities near the mines, such as Salar de Atacama in Chile, according to Azo Clean Tech. The composition of lithium batteries involves the use of potentially toxic materials like copper, nickel, and lead, and significant environmental problems can result from their improper disposal.
Introducing Oxygen-Ion Batteries & their Environmental Favorability
Addressing all these problems, oxygen-ion batteries, developed by the researchers at TU Wien, exhibit exceptional durability, eliminate the need for elements, and resolve fire hazard concerns. Positioning an oxygen-ion battery as a potential alternative to lithium-ion batteries, a significant breakthrough has been made at TU Wein, offering numerous advantages.
Allowing for an exceptionally long lifespan and regeneration, the energy density of oxygen-ion batteries may not match that of lithium-ion batteries, but their storage capacity does not diminish irreversibly over time. Making them an environmentally favorable option, scarce elements are not relied upon, and non-combustion materials are utilized in the production of oxygen-ion batteries.
Already, a patent application has been filed in collaboration with partners in Spain, realizing the potential impact of the innovative battery concept. The oxygen-ion batteries could provide an exceptional solution for large-scale energy storage systems, especially for storing electrical energy from renewable sources.
Drawing from the extensive experience of the TU Wein team in utilizing ceramics for fuel cells, ceramic materials have emerged as a new solution for the development of oxygen-ion batteries. The studied ceramic materials are capable of absorbing and releasing oxygen ions, facilitating the migration of these ions between materials, and generating electric current upon the application of electric voltage.
Potential Impact, Applications, Aging and Regeneration of Oxygen-Ion Batteries
According to the Vienna University of Technology (TU Wein), oxygen-ion batteries don’t experience any aging issues, ensuring their long-lasting effectiveness. While manufacturing oxygen-ion batteries, incombustible materials are used and rare elements are not required like lithium batteries, resulting in a significantly reduced environmental impact and the elimination of the risk of spontaneous explosions.
The ability of charge carriers diminishes over time in many batteries, leading to a decrease in battery capacity and a serious problem after numerous charging cycles. Oxygen batteries, however, do not have this problem.
By compensating for the loss of oxygen through the reactions by utilizing oxygen from the surrounding air, regeneration of oxygen-ion batteries can be achieved without any complication. Oxygen-ion batteries can be a suitable option for storing clean energy, despite a lower energy density compared to lithium batteries and operating temperatures between 392 and 752 degrees Fahrenheit.
Similar Post
Advantages in Energy Storage, Feasibility and Environmental Benefits
The oxygen-ion batteries offer an excellent solution for applications that require large-scale energy storage, such as temporary storage of solar or wind energy, due to their long service life, the ability to produce large quantities without rare elements, and their non-combustible nature.
Each with its unique advantages, other alternatives to lithium batteries, including sodium-based and sand batteries, are also under development. The non-flammable ceramic materials used in oxygen-ion batteries ensure a significant reduction in fire accidents compared to lithium-ion batteries.
Making the production of oxygen-ion batteries more feasible and cost-effective, the adaptability of ceramic materials allows for the replacement of challenging-to-obtain elements with alternatives. In order to replace lanthanum, currently used in the prototype of the oxygen-ion battery, which is neither rare nor abundant, more cost-efficient materials are aimed at being used.
As cobalt or nickel, commonly found in many batteries, are not utilized in oxygen-ion batteries, the environmental impact is further reduced. The decline in charge carrier mobility experienced by other batteries over time does not hinder the electricity generation capability of oxygen-ion batteries, which makes their exceptional longevity a crucial advantage of this new technology.
Expert Insights on Oxygen-Ion Batteries
Developed at TU Wein, the new battery concept has been designed primarily for energy storage purposes and may not be suitable for applications like electric cars or smart phones due to its lower energy density and operating temperatures.
Alexander Schmidt from TU Wein highlights that the strengths of oxygen-ion batteries, such as their long service life, large-scale production without rare elements, and absence of fire hazards, make them particularly valuable for energy storage in buildings and renewable energy systems.
Emphasizing the importance of their long service, the absence of rare elements, and their nonflammable nature, oxygen-ion batteries will be preferred when constructing large energy storage units, as the lower energy density and increased operating temperature of oxygen-ion batteries are not decisive factors.