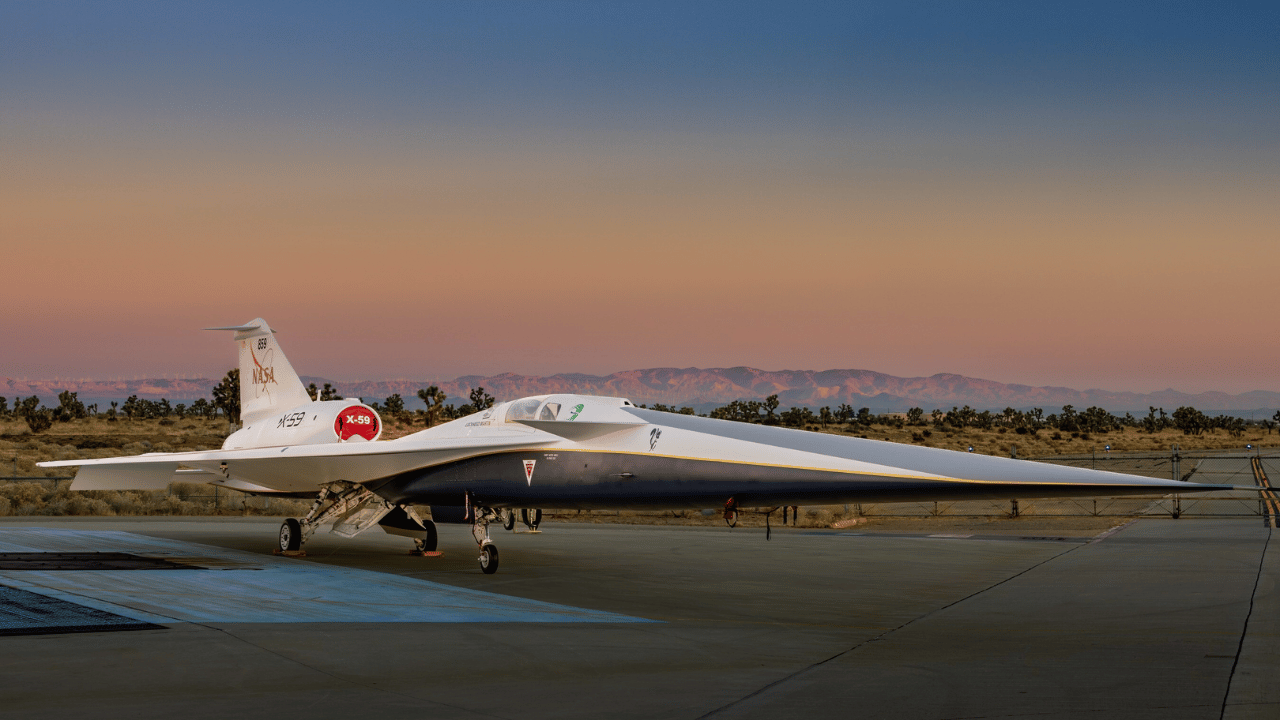
A much anticipated joint project between NASA and Lockheed Martin, the X-59 Quiet Supersonic Transport (QueSST) represents a major breakthrough in aeronautics, especially in tackling the difficulties of supersonic flight. The recently unveiled aircraft is a ground-breaking attempt to lessen the disturbing sonic boom that comes with travelling faster than supersonic.
The X-59 is distinguished by its distinctive design, especially its long, pointed nose-cone, which is essential in lowering the volume of the sonic boom to a mere “sonic thump.” However, this configuration makes it difficult to see forward from the cockpit. To solve this, the X-59 is equipped with an improved flight vision system (EVS), incorporating a 4K camera with a 33° by 19° angle of view.
By making up for the absence of a forward-facing window, this mechanism makes sure pilots can see clearly forward. The newest avionics from United Technologies subsidiary Collins Aerospace substantially improve the cockpit of the X-59. Among the avionics are the EVS with long-wave infrared sensors and the Pro Line Fusion Cockpit, which shows the sonic boom on the ground. While the NASA external vision system (XVS) gives the forward view, these sensors are essential for landing.
NASA’s X-59 is an important research instrument in addition to an experimental aircraft. The goal of the project is to make it possible for commercial supersonic flying over land, which is now impossible because of sonic boom noise and disruption. The X-59’s design seeks to achieve supersonic speeds of 1.4 times the speed of sound (about 925 mph) while delivering a gentler sonic thump instead of a typical boom.
The X-59’s development and debut are important because they address the cultural and environmental disruptions brought on by sonic booms, which have been a problem with aircraft like as the Concorde in the past. Due to the loud and disruptive sonic boom of the Concorde, its flights were mostly restricted to over-ocean routes. The goal of the X-59, on the other hand, is to make supersonic travel over land possible and less invasive.
The X-59 would go through extensive testing phases after its introduction, including engine runs, taxi testing, and integrated systems testing. The purpose of these testing is to get the aircraft ready for its first flight, which is slated for later in 2024. After the aircraft has completed its initial flight testing at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works, it will be moved to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Centre in Edwards, California, for additional operations and testing.
The construction and testing of the X-59 promise quicker travel times and less environmental effect, marking not just a significant advancement in aeronautical engineering but also a potential paradigm shift in air travel. Future rules and designs for will likely be greatly influenced by the information and understanding obtained from the X-59 project.
Following the unveiling, the next steps for the X-59 include comprehensive testing phases, such as integrated systems testing, engine runs, and taxi testing. These tests are crucial in preparing the aircraft for its first flight, scheduled for later in 2024. The initial flight tests will be conducted at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works, after which the aircraft will be transferred to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, for further operations and testing.
The X-59’s development and testing not only signify a leap in aeronautical engineering but also present a potential paradigm shift in air travel, promising faster travel times and reduced environmental impact. The data and insights gained from the X-59 project are expected to be instrumental in shaping future regulations and designs for commercial supersonic aircraft, thus opening new frontiers in aviation.
Near-Silent at 925 MPH: NASA and Lockheed Martin’s Advanced X-59 Supersonic Journey
Latest from Aviation

IndiGo Hits $23.3B Valuation: Indian Carrier Briefly Tops Global Airline Rankings with 13% YTD Stock Rally
India’s IndiGo has made aviation history this April, with its market cap hitting ₹2 lakh crore ($23.3 billion), briefly outpacing legacy carriers Delta Air Lines and Ryanair to claim the crown as

Qatar Airways Starlink Wi-Fi Reaches 80% on 777s, First to Equip A350s
Qatar Airways is completing its fleet-wide Starlink internet installation on Boeing 777 aircraft and will start equipping its Airbus A350 fleet this month, becoming the first airline globally to offer this technology
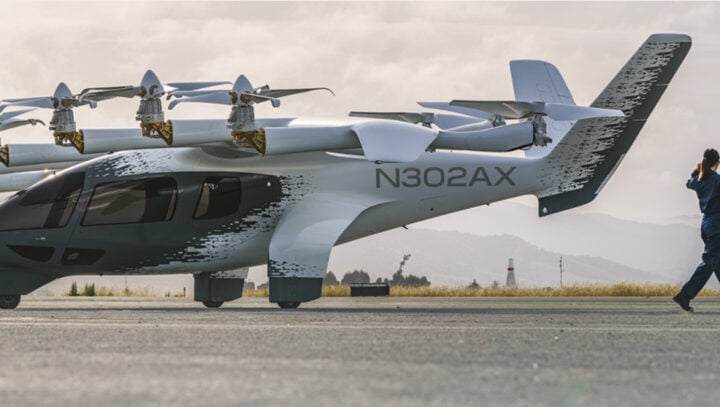

Ethiopian Airlines and Archer Aviation Partner to Launch Electric Air Taxi Network in Ethiopia
Ethiopian Airlines, Africa’s largest carrier, has signed an agreement with U.S.-based Archer Aviation to deploy electric air taxis in Ethiopia. The deal, valued at up to $30 million under Archer’s “Launch Edition”
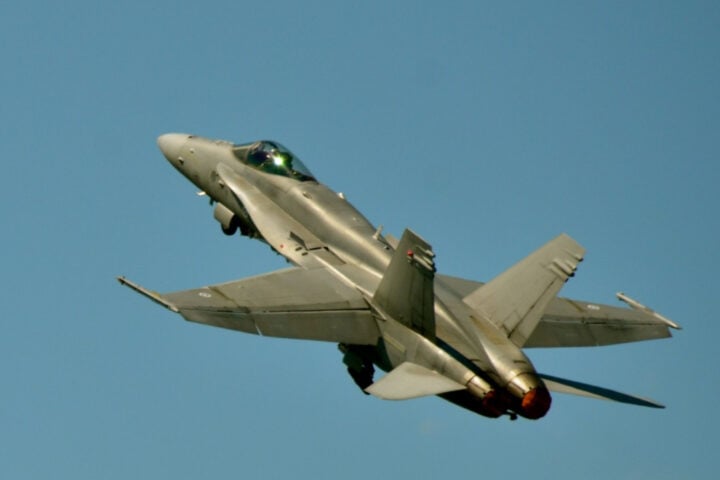

Boeing Secures $20B NGAD Contract for F-47 Fighter Jet
Boeing has secured a major victory in the aerospace defense sector by winning the contract for the U.S. Air Force’s Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) fighter jet program. The aircraft, now designated

Ryanair’s £79 ‘Prime’ Offers Up to £420 Savings
Ryanair, Europe’s largest budget airline, has introduced a new subscription service called “Prime,” promising significant savings for frequent flyers. The £79 annual membership offers exclusive benefits including free reserved seating, complimentary travel

Bristol Airport Ranks Third in UK for Car Park Quality with 4.5 Star Average Rating
Bristol Airport has secured third place among UK airports for car park quality and safety, according to a recent study by motoring company Blackcircles. With 82% of its car parks rated four
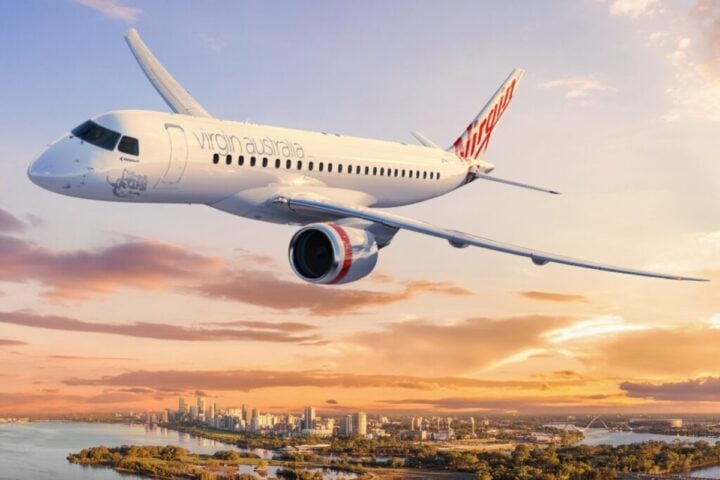

Virgin Australia’s 25% Off Flash Sale Features $45 Flights and Qatar Airways Partnership Benefits
Virgin Australia has unveiled a major flash sale slashing fares by up to 25% across 35 domestic and international destinations. The time-limited promotion features one-way fares starting from just $45 between Sydney
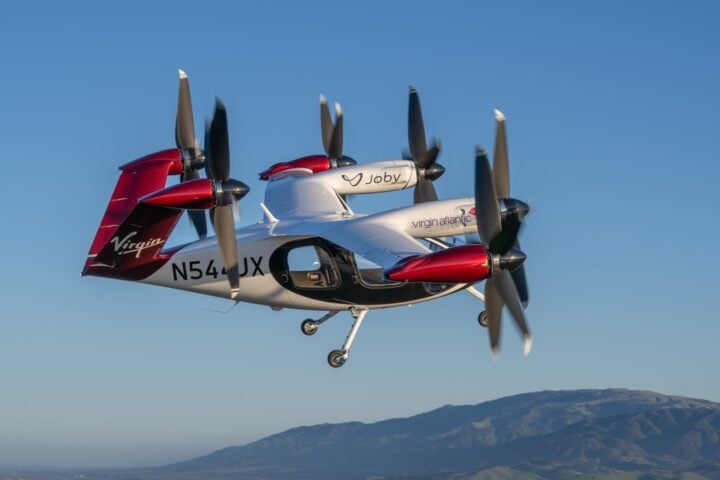

UK’s 8-Minute Air Taxi: Joby and Virgin Atlantic Partner for Electric Airport Transfers
Joby Aviation and Virgin Atlantic have announced a partnership to launch electric air taxi service in the United Kingdom, offering zero-emission flights that could dramatically reduce travel times between airports and city
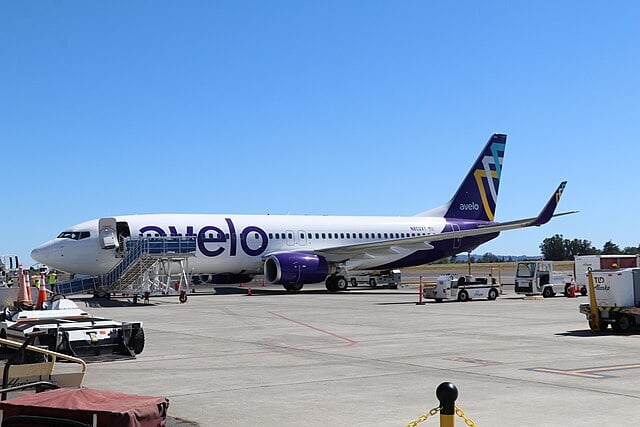

Avelo Airlines Adds Two Nonstop Routes from Grand Rapids, Connecting to Raleigh-Durham and Lakeland
Gerald R. Ford International Airport (GRR) has announced the addition of Avelo Airlines to its carrier roster, expanding service with two new nonstop routes to previously unserved markets. This development comes after

Breeze Airways Expands Florida Network with New Key West Routes
Breeze Airways, the low-cost carrier founded by aviation entrepreneur David Neeleman, is expanding its Florida presence with two new nonstop routes to Key West starting June 12, 2025. Flights will connect Key

Singapore Airlines and Scoot Ban In-Flight Power Bank Use Starting April 1
Singapore Airlines (SIA) and its budget carrier Scoot will prohibit passengers from using or charging power banks on flights beginning April 1, 2025. The airlines announced this safety measure on March 12
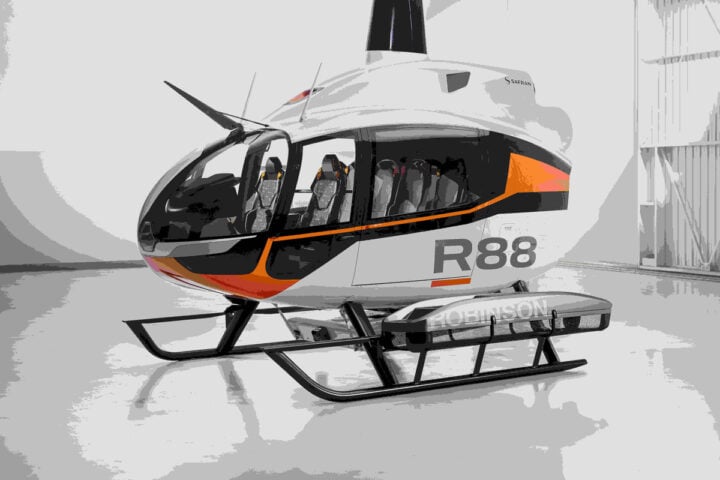

Robinson’s R88: 10-Seat Helicopter with 1,800-Pound Payload and 350-NM Range
Robinson Helicopter Company has launched the R88, its first all-new helicopter in nearly 15 years. This 10-seat single-engine rotorcraft pushes Robinson into new territory beyond its traditional light helicopter market. Breaking New
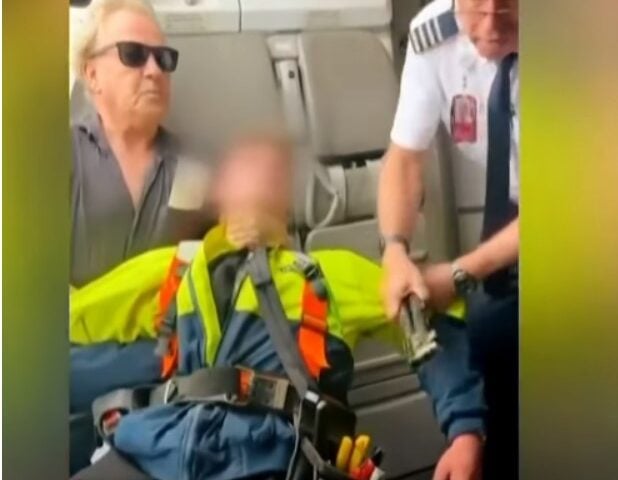

Armed Teen Breaches Avalon Airport Security: Passengers and Pilot Tackle 17-Year-Old with Loaded Shotgun
Incident Breakdown: What Happened at Melbourne’s Secondary Airport A severe security breach occurred at Avalon Airport on Thursday afternoon when a 17-year-old male allegedly attempted to board Jetstar flight JQ610 bound for

Qantas Flight QF643 Returns to Sydney After 18-Minute Delay as Cockpit Smoke Triggers PAN Call and Safe Emergency Landing with Zero Injuries
A Qantas Boeing 737-800 traveling from Sydney to Perth executed an emergency landing on Monday morning after smoke was detected in the cockpit minutes after takeoff, prompting immediate safety protocols and highlighting

Airlines Ban In-Flight Power Bank Use After Fire Destroys Aircraft
Major airlines are introducing stricter rules for power banks following several concerning safety incidents, including a fire that led to an emergency evacuation on an Air Busan plane earlier this year. Eva


