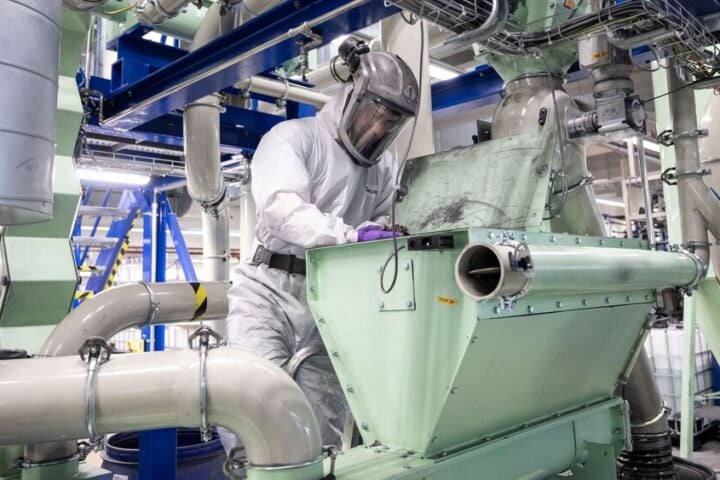
NASA’s researchers at Solid-state Architecture Batteries for Enhanced Rechargeability and Safety (SABERS) have made a new leap in developing a high-performing battery for electric aircraft. Batteries and their performance have been a major issue in the quest for sustainable electric airplanes.
The new solid-state battery is lighter and can store more power than lithium-ion batteries. NASA’s recent breakthrough has made solid-state batteries suitable for use in large scale electronics. One of the key advantages of lithium-ion batteries is their ability to discharge power much swifter than solid-state batteries.
SABERS may have solved this issue by improving the discharge rate of solid-state batteries by a factor of 10 and then an another additional factor by five. This new frontier of battery innovation could perform much better than lithium-ion batteries can, as per Rocco Viggiano, principal investigator for SABERS at NASA’s Glenn Research Center.
The newer battery design makes the battery 30 to 40 percent lighter and enables the performance to double or triple i.e. the energy it can store. Safety is a crucial concern for aircraft, and solid-state batteries have a better advantage over lithium-ion batteries as it is void of any liquids and can still be used even when damaged. Solid-state batteries can function in twice as much temperatures as lithium-ion batteries and require less cooling technology.
- Tesla Delays Affordable Model Y Production to Late 2025 Amid EV Market Pressure
- Aldi Pork Carnitas Alert: FSIS Warns of Metal Contamination in 16-Ounce Packages with June-July Use Dates
- Protected: Weekly Mailer Task
- GP Registration Online Now At 98.4% Of Practices As 3.8 Million Sign Ups Signal NHS Digital Shift
- Protected: Update the social media status in Content Calendar
The various aviation players and the U.S. government are keen on this promising battery technology to reduce air pollution. Although not yet commercially usable, NASA researchers are partnering with academic frontiers to continue developing this battery technology.