The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) will receive assistance from a small satellite called Monitoring Activity from Nearby Stars with UV Imaging and Spectroscopy (MANTIS). MANTIS, an $8.5 million cubesat selected by NASA, will work alongside the JWST to enhance the search for potentially habitable exoplanets. JWST focuses on analyzing the atmospheres of rocky planets that could support life, while MANTIS is designed to observe star activity, including flares. Expected to launch in 2026, MANTIS will make observations in the full range of ultraviolet light, including extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light, which is more energetic.
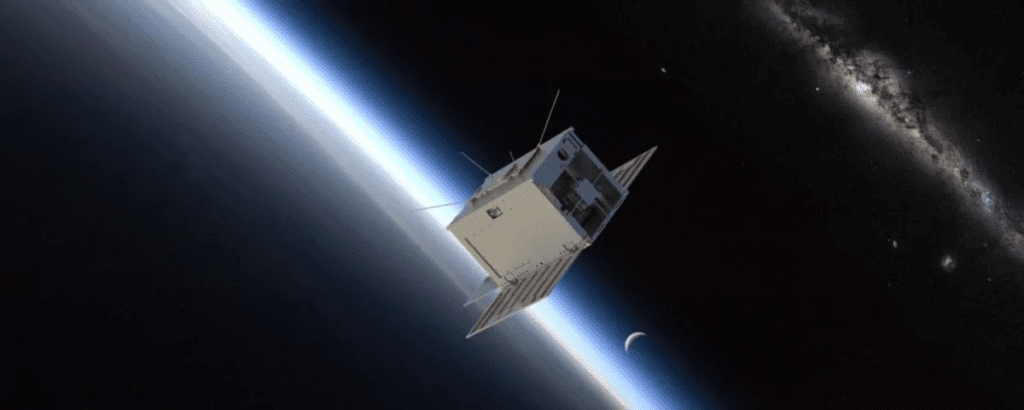

It will study stars located several light-years away from Earth, complementing the JWST’s observations of exoplanets. It will be the first mission to examine the sky in the extreme ultraviolet range since NASA’s retired Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer in 2001. MANTIS aims to refine the theory that rocky exoplanets with water on their surfaces face challenges if they orbit very active stars, which expose them to significant radiation. Over the course of a year in Earth orbit, MANTIS will provide data to improve understanding in this area. The spacecraft will carry two telescopes: one optimized for lower-energy ultraviolet radiation and another designed specifically for the extreme ultraviolet range. This will enable MANTIS to capture images of stars in extreme ultraviolet light for the first time, providing important context about the stellar environments where exoplanets exist.
Similar Post
MANTIS is envisioned as an ultraviolet sidekick to the JWST, observing the same targets and filling in critical information about the stellar environments surrounding exoplanets. It will contribute to measuring the release of extreme ultraviolet radiation from planets, which can indicate potential atmospheric loss. By studying stars in extreme ultraviolet light, MANTIS aims to offer tantalizing insights into worlds that may be capable of supporting life. The mission builds on technology from two other university cubesats: the Colorado Ultraviolet Transit Experiment (CUTE), launched in 2021 for exoplanet observations, and the Supernova Remnants and Proxies for ReIonization Testbed Experiment (SPRITE), scheduled to study star explosions in 2024. Once operational, MANTIS will provide valuable data on how stellar energy impacts the atmospheres of nearby planets, particularly those of similar size to Earth that may be habitable.