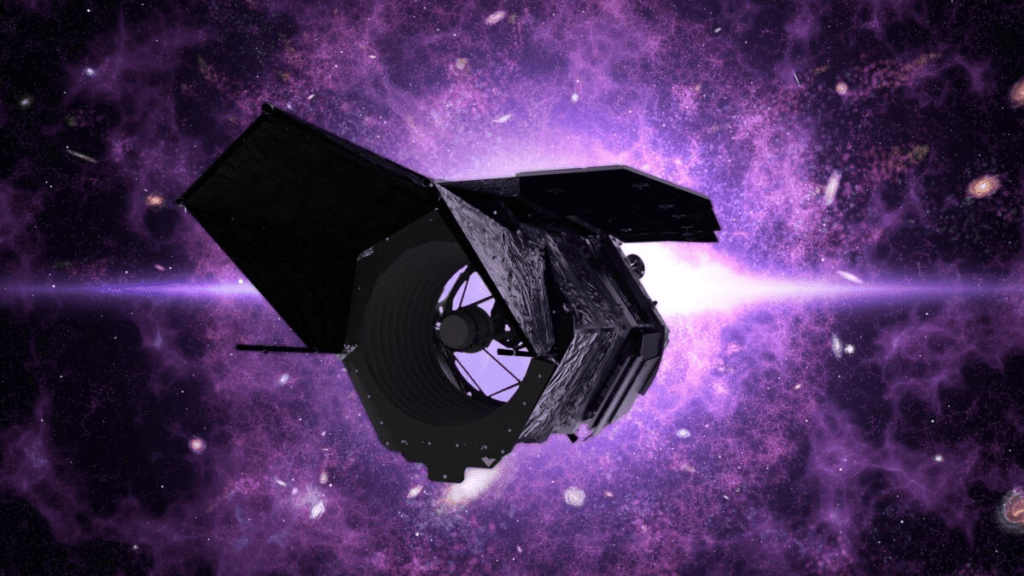
The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope, also known as Roman, would be able to look at vast areas of space to help cosmologists analyze the universe on a large scale.
Roman will be very different from telescopes like Hubble and James Webb, aiming to capture a broad view of the sky.
In order to solve cosmic mysteries on bigger scales, a space telescope that can provide a far larger view is needed & that’s exactly what Roman is designed to do.
Roman will be assigned for tasks like estimating how many exoplanets exist in the entire galaxy and figuring the distribution of galaxies to help understand dark matter.
One of the biggest advantage Roman has for this sort of tasks, along with its wider view, is that it will capture images swiftly.
As per NASA, Roman will be able to map the cosmos up to 1,000 times faster than Hubble could.
“Roman will take around 100,000 pictures every year,” mentioned Jeffrey Kruk, research astrophysicist at Goddard Space Flight Center
Compared to Roman’s larger field of view, it would take longer than our lifetimes for powerful telescopes like Hubble or Webb to cover as much sky.
Roman is set to revolutionize telescopes along with our understanding of the universe and unlock secrets that have remained hidden until now.