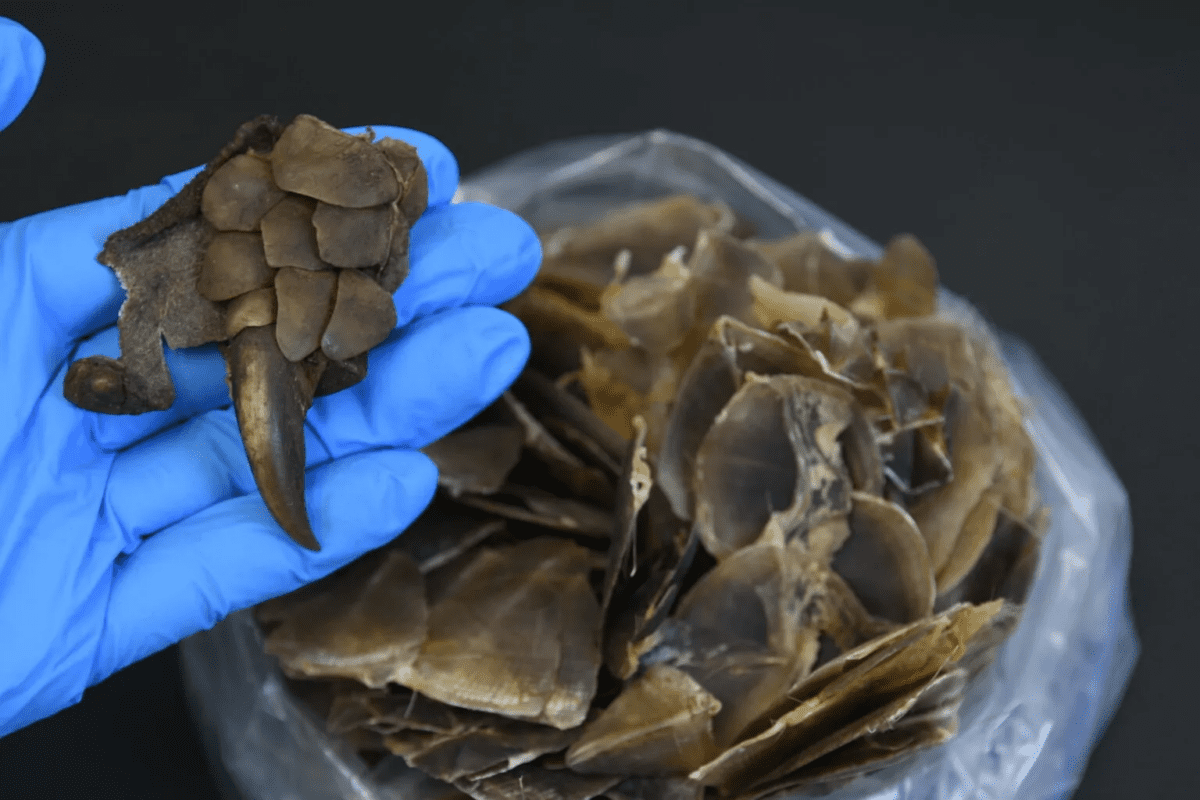
Unveiling a chapter unknown in the realm of biodiversity, a groundbreaking study published on September 25, 2023, has brought to light a previously unrecognized pangolin species, marking the count at nine. This revelation, a blend of genomic analysis and morphological evidence, opens up a fresh perspective on the diversity and evolutionary journey of pangolins.
Led by dedicated scientists including Tong-Tong Gu and Li Yu, and meticulously edited by William J. Murphy from Texas A&M University, the research journey was nothing short of an adventure. The initial spark of discovery was ignited by unassignable mitochondrial haplotypes found in confiscations in Hong Kong, whispering tales of an unknown species. Further expeditions in Yunnan unearthed additional haplotypes aligning with this mysterious creature, strengthening the hypothesis.
Diving deep into the genetic world, a comprehensive analysis of 138 whole genomes and scale characteristics was conducted, representing all recognized pangolin species and the cryptic new one. This enigmatic species revealed distinct genomic signatures, narrating a story of separation from the Philippine and Malayan pangolins over 5 million years ago. “Our morphometric results clearly attributed this cryptic species to Asian pangolins,” shared the researchers, their voices filled with the excitement of discovery.
Laying down a robust genomic foundation, the study advocates for a new taxonomic classification of pangolins, welcoming the newly discovered species, named Manis mysteria, as the fifth Asian pangolin. However, the genomic data paints a concerning picture, indicating lower heterozygosity, higher inbreeding level, and genetic load, signaling a population in decline. These findings bring to the forefront the urgency of conservation efforts to safeguard this enigmatic species from vanishing into extinction.
Similar Posts
Supported by various institutions, including the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Animal Branch of the Germplasm Bank of Wild Species of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the research was a collaborative endeavor. A nod of acknowledgment was given to Dr. John Blackwell and his colleagues for polishing the English of the manuscript, ensuring clarity in communication.
Exploring beyond the genetics, the study delves into the impact of glacial climate changes and recent anthropogenic activities driven by illegal trade on the species. The echoes of these factors are inferred to have contributed to the population decline of the newly discovered pangolin, highlighting the delicate balance of nature.
Expanding our understanding, the research sheds light on the diversity of pangolins and their evolutionary journey. It draws attention to the vital implications of these findings for conservation strategies, aiming to prevent the extinction of this species in the wild. The research team, armed with advanced genomic tools and methodologies, analyzed the DNA sequences and mitochondrial genomes of the pangolins, unveiling morphological evidence of the new species.
Highlighting the significance of scientific innovation, the study uncovers hidden biodiversity and enhances conservation efforts. The discovery of Manis mysteria brings attention to the rich biodiversity that remains unexplored and underscores the importance of protecting endangered species. Contributing valuable knowledge to the scientific community, the research aids in the development of informed conservation policies.
Emphasizing the role of genomic analysis in species identification and understanding evolutionary patterns, the study demonstrates the potential of integrating genomic data with morphological characteristics to uncover cryptic species. The revelation of a new pangolin species underscores the need for continuous exploration and research in biodiversity.
Facing challenges including illegal trade and habitat loss, pangolins are in immediate need of conservation action. The study serves as a reminder of the untapped mysteries of the natural world and the discoveries awaiting scientific inquiry. Providing a basis for further research on pangolin species and their conservation needs, the discovery of the ninth pangolin species adds a new dimension to the understanding of pangolin evolution and diversity.
The research emphasizes the importance of addressing the critical issues faced by endangered species through informed conservation strategies. Shedding light on the impact of human activities on pangolin populations, the study calls for sustainable practices. Offering a glimpse into the hidden diversity of the animal kingdom, the findings underscore the significance of preserving it.
Serving as a testament to the advancements in genomic analysis and its role in species discovery, the study calls for a reevaluation of conservation priorities to include the newly discovered pangolin species. The findings underscore the importance of scientific collaboration in advancing knowledge and addressing conservation challenges.
Highlighting the role of technology in uncovering the mysteries of biodiversity and enhancing conservation efforts, the study contributes to the growing body of knowledge on pangolins and their conservation needs. The discovery of Manis mysteria is a significant milestone in the field of biodiversity research and conservation.
Offering insights into the evolutionary history of pangolins and the factors contributing to their population decline, the study calls for collective efforts to protect the newly discovered pangolin species and preserve biodiversity for future generations. With a pangolin conservation spirit, wildlife buff spontaneity, and a concerned tone, let’s join hands to protect these enigmatic creatures and preserve the wonders of our natural world.
On September 25, 2023, a groundbreaking revelation danced through the scientific community, unveiling a ninth, previously hidden member of the pangolin family, Manis Mysteria, a whisper of the wild unknown.





![Representative Image: European Starling [49/366]. Photo Source: Tim Sackton (CC BY-SA 2.0)](https://www.karmactive.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/Starlings-Drop-82-in-UK-Gardens-as-Birdwatch-2025-Reveals-Record-Low-Count-Since-1979-720x480.jpg)










