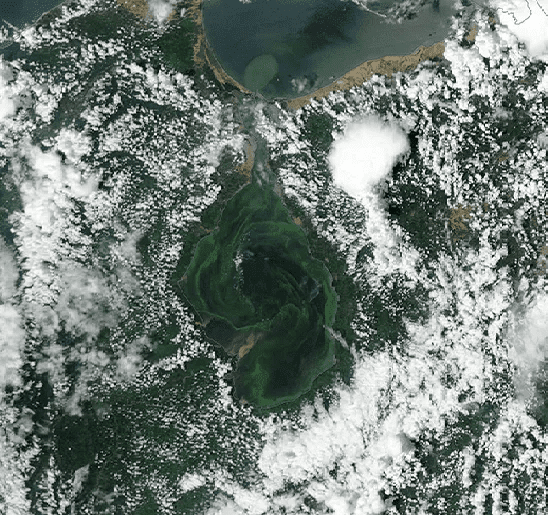
Venezuela’s Lake Maracaibo, once a symbol of its oil boom, now showcases the effects of industrial neglect and environmental damage. Spanning tens of thousands of square kilometers, Lake Maracaibo is among the world’s oldest and largest lakes. Historically, it was a vital resource for the Venezuelan oil industry, with its bed crisscrossed by an intricate network of pipes. But decades of excessive oil exploitation, coupled with outdated infrastructure and a lack of waste treatment facilities, have turned this natural wonder into an ecological nightmare.
The lake’s degradation began in earnest in the 1930s when a canal was carved at its northern end, allowing large oil tankers to traverse its waters and connect to the open sea. This move, while economically strategic, introduced seawater into the lake, disrupting its freshwater ecosystem. The repercussions of this decision are still felt today, with the lake’s delicate balance further skewed by continuous oil spills and the unchecked dumping of wastewater.
Rainwater from over a hundred tributaries flows into Lake Maracaibo, turning it into a receptacle for several states’ waste, including the Colombian department of Norte de Santander. The unchecked inflow of fertilizers, sewage, and other pollutants has led to alarmingly high concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus. These nutrients, essential for plant growth in moderation, have in excess spurred the rampant proliferation of toxic microalgae, specifically cyanobacteria.
Known locally as “verdin,” this toxic algae is not just an environmental concern but a public health hazard. Cyanobacteria produce toxins detrimental to aquatic life, leading to massive fish die-offs. For the local fishing community, this translates to dwindling catches and an uncertain future. Moreover, humans exposed to these toxins report ailments ranging from skin rashes to more severe health issues.
Similar Post
The situation is further exacerbated by the lake’s transformation into a “septic tank.” Environmentalists have often cautioned against polluting the lake. Today, those warnings are a grim reality, with the lake’s shores witnessing frequent oil spills, the spread of unpleasant odors, and the ever-growing dominance of toxic microalgae. While the narrative so far paints a bleak picture, it’s essential to understand that Lake Maracaibo’s plight is emblematic of broader global environmental challenges. The story underscores the urgent need for sustainable practices, not just in Venezuela but worldwide. It’s a call for countries to value the environment more than quick profits.
Immediate, comprehensive action is the need of the hour. This includes not just clean-up efforts but also addressing the root causes of the pollution. Modern infrastructure, stringent regulations, and a collective commitment to environmental stewardship can potentially reverse some of the damage inflicted upon Lake Maracaibo. Lake Maracaibo’s situation highlights the delicate balance between nature and human actions. As global environmental concerns rise, such stories urge us to take action quickly. The lake’s uncertain future reminds us of the larger sustainability challenges we face.