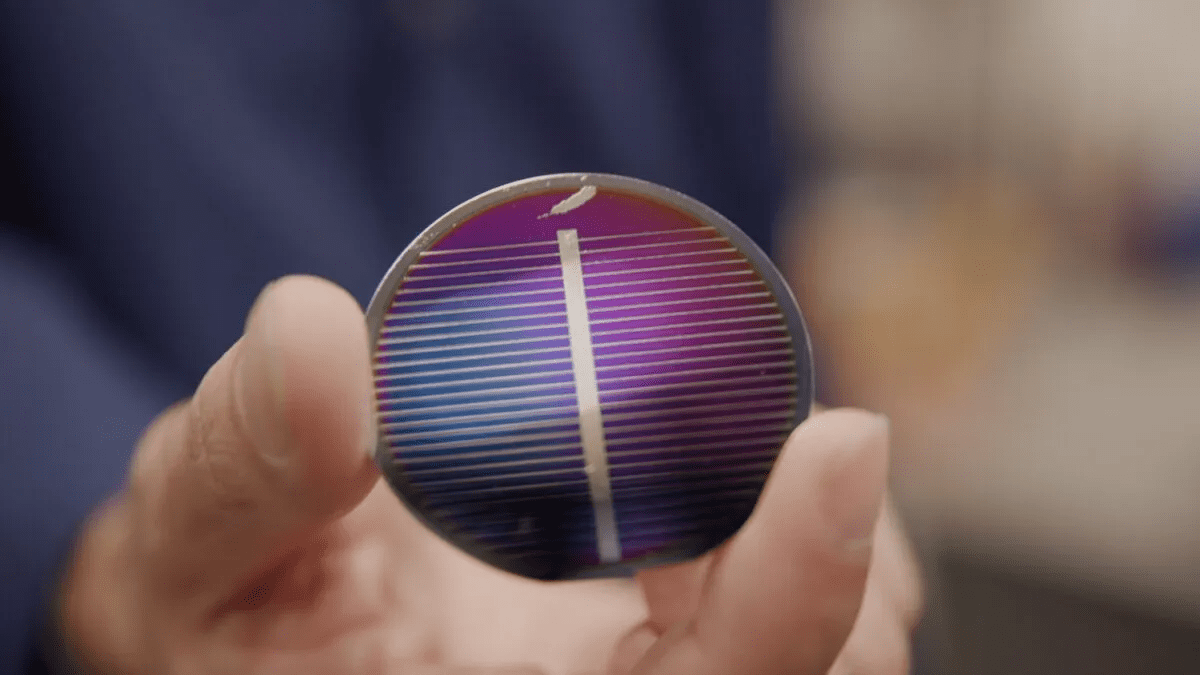
Blue Origin, the space company founded by Jeff Bezos, has developed a technique called Blue Alchemist to produce solar cells and transmission wire using only lunar regolith. The method could help NASA establish a sustainable human presence on the moon, and reduce the cost of transporting materials. The Blue Alchemist method uses molten electrolysis to extract the materials for solar cell construction from aluminum, iron, and silicon in lunar regolith. Once demonstrated and implemented, Blue Origin claims that the method will provide unlimited solar power. The solar cells produced can operate for over a decade in the moon’s “harsh environment.” Blue Origin is working on the development of its New Glenn rocket, which will be used to launch a science mission to Mars. The company has also been selected by NASA to provide its Orbital Reef space station.
Turning moon dust into solar power with Blue Alchemist
Blue Origin has announced that it has created a method for producing solar cells and transmission wire using only lunar regolith. The technique, called Blue Alchemist, uses molten electrolysis to extract the materials for solar cell construction from aluminum, iron, and silicon in lunar regolith. In a statement, the company explained that it has demonstrated its method’s viability and has “been making solar cells and transmission wire from regolith simulants.” The company added, “once demonstrated and implemented on the Moon, Blue Alchemist will put unlimited solar power wherever we need it.”
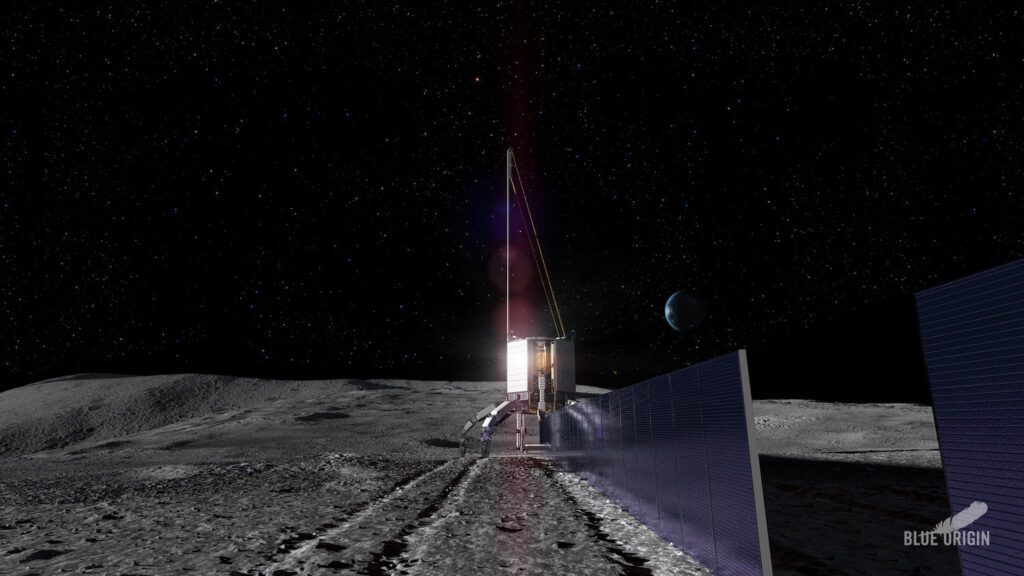

NASA’s ambition to establish a sustainable human presence on the moon
NASA’s Artemis program aims to establish a sustainable human presence on the moon. To achieve this, humanity will need to use local resources, and that is where Jeff Bezos’ space company, Blue Origin, hopes to contribute with its Blue Alchemist solar project. Blue Origin’s method could dramatically cut costs associated with transporting materials to the moon while providing a robust solution. In its statement, Blue Origin says its solar cells can operate in the moon’s “harsh environment” for over a decade.
The benefits of using lunar regolith
Lunar regolith is the surface material found on the moon. It’s different from Earth soil, as it’s a mix of dust, rock chips, minerals and glass. To get the materials for the solar cell, Blue Origin used a combination of extreme heat and electricity. Silicon is a key ingredient for the solar cell, and the process creates an extremely pure version of silicon suitable for solar. Blue Origin says its method doesn’t require the toxic chemicals that are often used for silicon purification on Earth.
The significance of Blue Alchemist
The Blue Alchemist method could prove to be a vital part of NASA’s mission to establish a permanent presence on the moon as part of its Artemis program. Blue Origin has demonstrated the viability of the method, and once implemented on the Moon, it could provide unlimited solar power wherever it’s needed. Blue Origin’s method could also help reduce the cost of transporting materials to the moon while providing a robust solution.
- Malta Human History Pushed Back 1,000 Years as 8,500-Year-Old Seafaring Evidence Surfaces
- Trump Backs Coal With $200B Loans and EPA Delays Amid 60-Year Low in U.S. Output
- Teen Screen Time Above 2 Hours Linked to Anxiety, Depression, and Cognitive Decline
- Cruise Ship Pollution Includes Sewage, Gray Water, Microplastics, and Chemical Discharge at Sea
- World Book Day 2025: UNESCO’s ‘Read Your Way’ Theme Highlights Rio de Janeiro and Indigenous Languages
What Ahead
Blue Origin’s creation of a method for producing solar cells and transmission wire using only lunar regolith is a significant achievement that deserves more recognition. The working prototype solar cell provides a glimpse into a path forward to realizing Blue Origin’s vision of unlimited solar power on the moon. The solar cells can operate for over a decade in the moon’s harsh environment, and once implemented, the Blue Alchemist method will provide unlimited solar power wherever it’s needed. By harnessing the resources already on the moon, Blue Origin’s method could help reduce the cost of transporting materials and provide a robust solution.