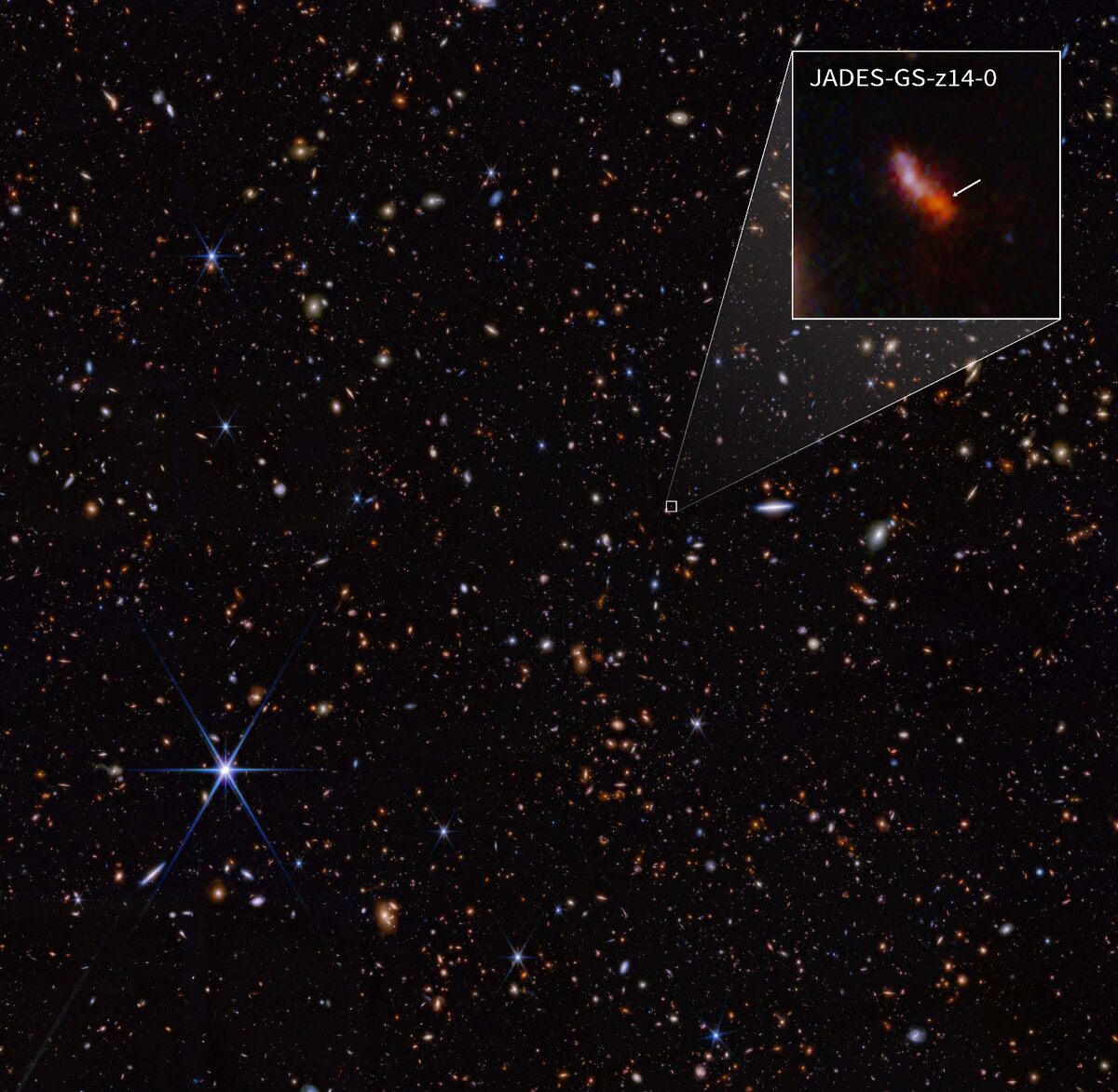
The James Webb Space Telescope observed what would be the oldest known galaxy, only 290 million years after the Big Bang, and the presence of oxygen has been detected.
Scientists were surprised to discover that one of the galaxies, JADES-GS-z14-0, had a redshift of 14.32, making it the new farthest known galaxy. Webb has broken the record several times, but the light reaching us from this galaxy was emitted when the universe was only 290 million years old, meaning we are traveling 13.8 billion years into the past.
Surprisingly bright. The light from JADES-GS-z14-0 is “surprisingly bright,” says the Webb team of astronomers. “We wouldn’t expect for such a distant galaxy, and it was very close to another galaxy such that the two appeared to be part of one larger object.”
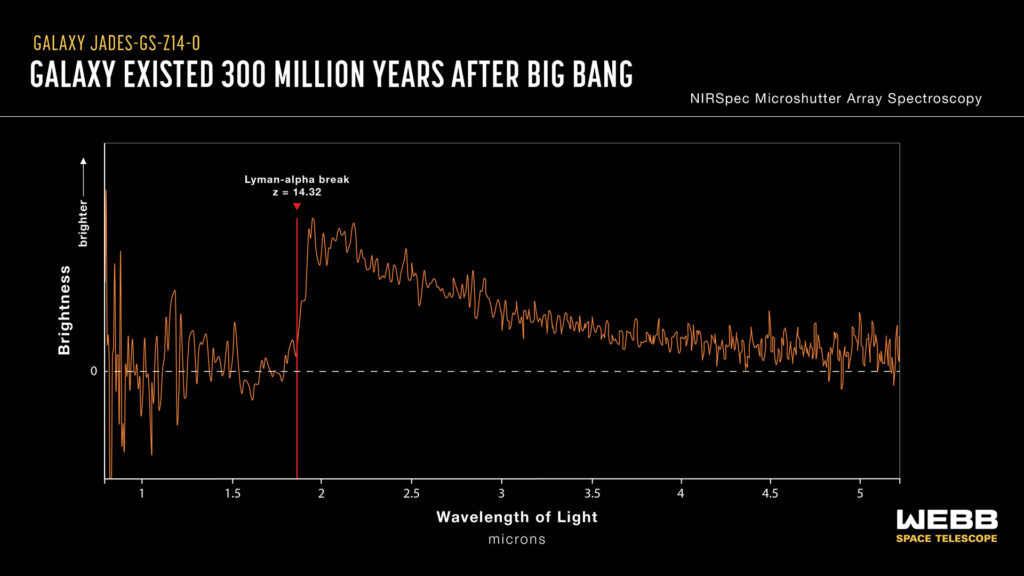
According to the astronomers, the images suggest that the source is over 1,600-light years across. Which proves that the light we see is coming is not from emission near a growing supermassive black hole but mostly from young stars. This hints at the size of the galaxy being several hundreds of millions of times the mass of the Sun. “This raises the question: How can nature make such a bright, massive, and large galaxy in less than 300 million years?” the astronomers question.
The spectrometer revealed that the galaxy’s color is not as blue as one might expect, indicating that some of the light is reddened by dust, despite the early age of the universe. The MIRI camera, which covers longer wavelengths, also indicated the presence of strong emissions of ionized gas in the form of bright emission lines of hydrogen and oxygen in the galaxy.
Similar Post
Astronomers call this time Cosmic Dawn: the period when the first galaxies were born. The presence of oxygen detected so early in the galaxy’s life suggests that multiple generations of stars were already living and dying before Webb’s observations. These galaxies provide vital insights into how gas, stars, and black holes were changing when the universe was very young.
Discovering and studying galaxies so distant is made possible by the unprecedented resolution enabled by the Webb telescope in the infrared. Scientists took the images that make up this deep field between October 2023 and January 2024, and they are already writing science that still needs to be peer-reviewed. Some preliminary results can be read on the Webb telescope website, a joint project of NASA, ESA, and the Canadian Space Agency.