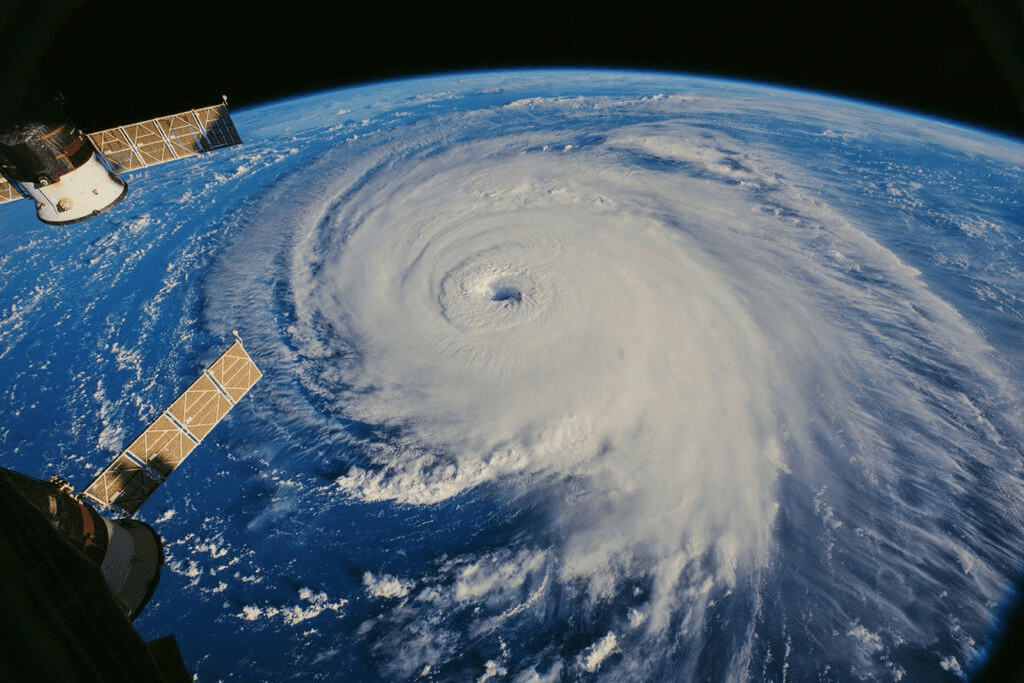
In recent decades, international environmental regimes have arisen to address variety of issues ranging from atmospheric problems like acid rain or the seasonal thinning of the stratospheric ozone layer, marine problems like oil pollution from offshore platforms and tankers, to terrestrial problems like desertification in drought-stricken areas or tropical deforestation. Satellites Helping Mitigate Climate Crisis In all these cases, efforts to come to terms with the relevant problems require international (often global) responses designed to limit human interference. To understand it’s range, remote-sensing data from different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum and images are acquired. In other words, earth observation by satellite remote sensing provides a powerful tool for monitoring various features of the Earth’s environment.
Various organisations like NASA, NOAA, ISRO and ESA use satellite data to monitor greenhouse gases concentration in the atmosphere, weather patterns, vegetation health, melting of glaciers and polar ice, bleaching of coral reefs, ocean acidification, changes in wildlife migratory patterns, and many other environmental indicators. Satellites not only monitor global environments, but technological innovations such as miniaturisation of sensors, high-speed data transfer, and upgraded storage capacity have revolutionized climate science. Satellite images used to monitor coral reefs using AI-backed methods, can not only map the location of a reef but also determine whether a reef is healthy or dying. This is done by analysing new algae growth and picking out bleaching events from the satellite data itself. NASA’s Fire Information for Resource Management System(FIRMS) uses near real-time data from MODIS to help guide the rescue missions in times of wildfires. Satellite imagery analysis can also enable us to point out if there has been severe deforestation in any area which might be leading to the effects of global warming. Prediction of hurricanes, droughts, and floods are other areas where analysis of satellite imagery is extensively applied.
Satellites monitor forest cover worldwide generating global datasets to predict trends and areas where deforestation occurs. According to NASA Earth Observatory, once home to 208,000 km² of forest (about 51.4 million acres), the State of Rondônia in western Brazil is now one of the most deforested parts of Amazon. Another problem that is less related to climate change and more to environmental degradation is plastic pollution, which can also be tracked with satellites. It is predicted that by 2050 there will be more plastic in the ocean than fish. The European Space Agency’s Sentinel-2 satellites can distinguish plastic debris from other materials, it’s concentration, movement and even sometimes origin with high accuracy. With other technological innovations – including drones and high-resolution satellites – it will be easy and quick to monitor global marine plastic pollution, thus helping clean-up operations and regulation.
With other factors like melting of ice sheets and desertification Satellites have thus allowed us to study the cryosphere and land degradation as the most fundamental and influential factors of climate crisis. According to The United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), desertification is now a global social and environmental problem.
Modern Satellites Helping Mitigate Climate Crisis with a range of sensors provide new and valuable perspectives on our planet. These perspectives allow us to understand large-scale changes in our environment and how to best protect it. To understand it best, here are few examples:
- Maxar technologies: Maxar is a leading space technology and intelligence company and here it shows illegal gold mining in the rivers of Amazon rainforest. The activity contaminates the river and the tributaries with mercury, slowly poisoning the life inside the rivers.
- Copernicus: Copernicus is the European Union’s Earth observation programme coordinated and managed for the European Commission by the European Union Agency for the Space Programme in partnership with the European Space Agency, The constellation provides emergency Earth imaging for disaster relief under the International Charter for Space and Major Disasters. To give an example this satellite image obtained by one of Copernicus sentinel-3 satellites on 15 March, 2022 shows the Sahara dust cloud engulfing the skies over western Europe.
- DLR: The German Aerospace Center, abbreviated DLR, is the national center for aerospace, energy and transportation research of Germany. The earth observation center (EOC) DLR research group used satellite data to accurately estimate tree loss. The earth observation satellites Sentinal-2 and Landsat-8 shows the tree loss due to unusual heat and draughts and harmful insect infestations along with other natural calamities to be the main triggers because of climate change.
- NASA has begun its mission known as “Global Climate Change: Vital Signs of the Planet”. This mission focuses only on climate change and related issues. It provides vital info on the developing situation around global warming and climate crisis.
- African nations are also stepping up by extending their space program into marine, climate and weather related applications.
- The Indian government will be providing necessary support via ISRO to small island nations to mitigate the effects of climate change. Indian PM Narendra Modi declared the initiative A.K.A ‘Infrastructure for Resilient Island States’ (IRIS) at the COP26 2021 meet.