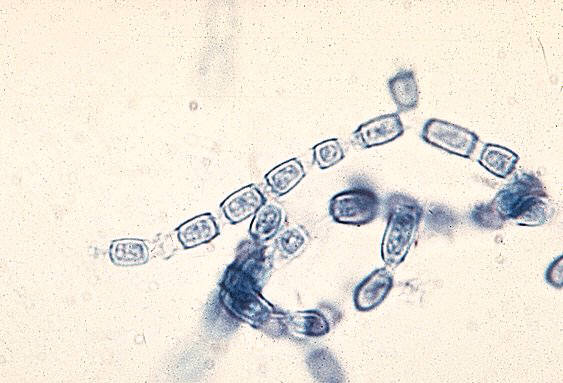
Prevalent in the southwestern US, parts of Mexico, and Central and South America, Coccidioides, a form of fungus, can potentially cause severe infections, ranging from pneumonia to meningitis, when its spores are inhaled from disturbed soil. Fungi, which include the Coccidioides, can be detrimental to human health, causing immense harm. Certain strains of fungi have the potential to cause diseases. Valley Fever, caused by Coccidioides is concluded to be potentially amplified by climate change.
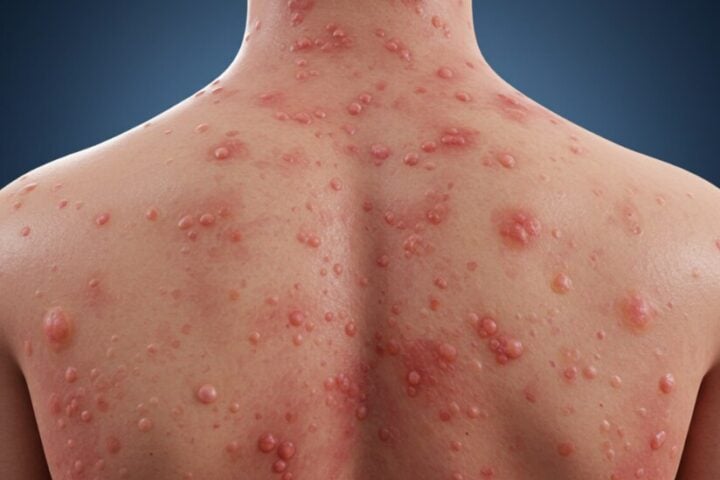
The symptoms of Valley Fever may be mild, which makes their detection and treatment delayed or neglected. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, severe or long-term problems develop in 5 or 10% of those who contract Valley Fever. The infection can also spread to other body parts, such as the brain, skin, or bones, which is about 1 percent of the time. The fatalities from Valley Fever are relatively rare, but lifelong anti-fungal treatments are still required for those who recover from the fever.
With a limited number of options available for antifungal drugs, the lack of vaccines, and the difficulties in diagnosing fungal diseases, a new fungal pathogen can have catastrophic implications. The cases of Valley Fever are also expected to increase as the fungus moves eastward from Texas to northward up to Washington State. Recent Studies have confirmed the expansion of Coccidioides, which, as mentioned before, was triggered by climate change and dust storms. It is therefore crucial to understand fungal spores, which can be multiplied easily and spread across vast continents, when assessing the potential threat to the fungi.
The World Health Organization listed Cryptococcus neoformans, a fungus whose spores can potentially infect the lungs and brain, as a top health hazard and hence to be paid attention to in 2022. The fungi can cause severe morbidity and mortality. The US CDC has also reported over 20,000 cases of Valley Fever caused by the Coccidioides fungus in 2019, causing an average death of 200 Americans each year. Certain strains of fungi like Cryptococcus and Coccidioides are capable of thriving in warm body temperatures, are dangerous, and have the potential to infect and affect healthy immune systems. Other notable fungi capable of causing disease in humans include strains of Aspergillus, Histoplasma, and Blastomyces.
Similar Posts
Fungal spores usually manifest as a silent, omnipresent threat, with each breath that we take carrying a large number of spores. But even though they appear risky, only a few fungal species can grow successfully inside humans, with fewer surviving in the immune system. Fungal spores can act as bioreactors that transform a loaf of bread into a mold-infested product within a day, which demonstrates the quickness with which they reproduce and survive.
In general, fungi pose no real threat to humans, but several hundred species can potentially infect us, viewing us as a food source much like a loaf of bread. The potential of emergent fungal pathogens, carried by hurricane winds or through global trade, underscores the need for increased vigilance and prevention efforts. The Fungal Spores are capable of certain diseases and are responsible for the significant outbreak at the paper mill in Michigan in 2023, which portrays a real threat to these organisms.
Fungal spores are resilient, can survive extreme conditions, and can even handle space travel. Despite the significant role of fungal spores in disease propagation, they remain a largely overlooked area when discussing fungal pathogens. With conditions like Valley Fever, early detection and timely treatment are significant. Therefore, increasing awareness is necessary. Future strategies for containing and preventing fungal infections should be heavily grounded in understanding the strength and movements of these fungal spores, which are extremely potent and resilient.