The European Union’s economic status is shrinking, accounting for just 13.3% of global gross domestic product compared with more than 20% in 1993. Its false sense of unity and strength are being dismantled by the world due to the inevitable rise of global tensions, technological advancements, and economic volatility. Brexit, the war in Ukraine, and the rise of populism are just some of the few problems it faces.
In response to these challenges, the European Commission has recently introduced a series of initiatives aimed at bolstering the EU’s economic security. These measures are part of a broader strategy to fortify the bloc’s resilience against economic coercion and technological espionage, ensuring both the security and sustainability of the EU’s economic landscape.
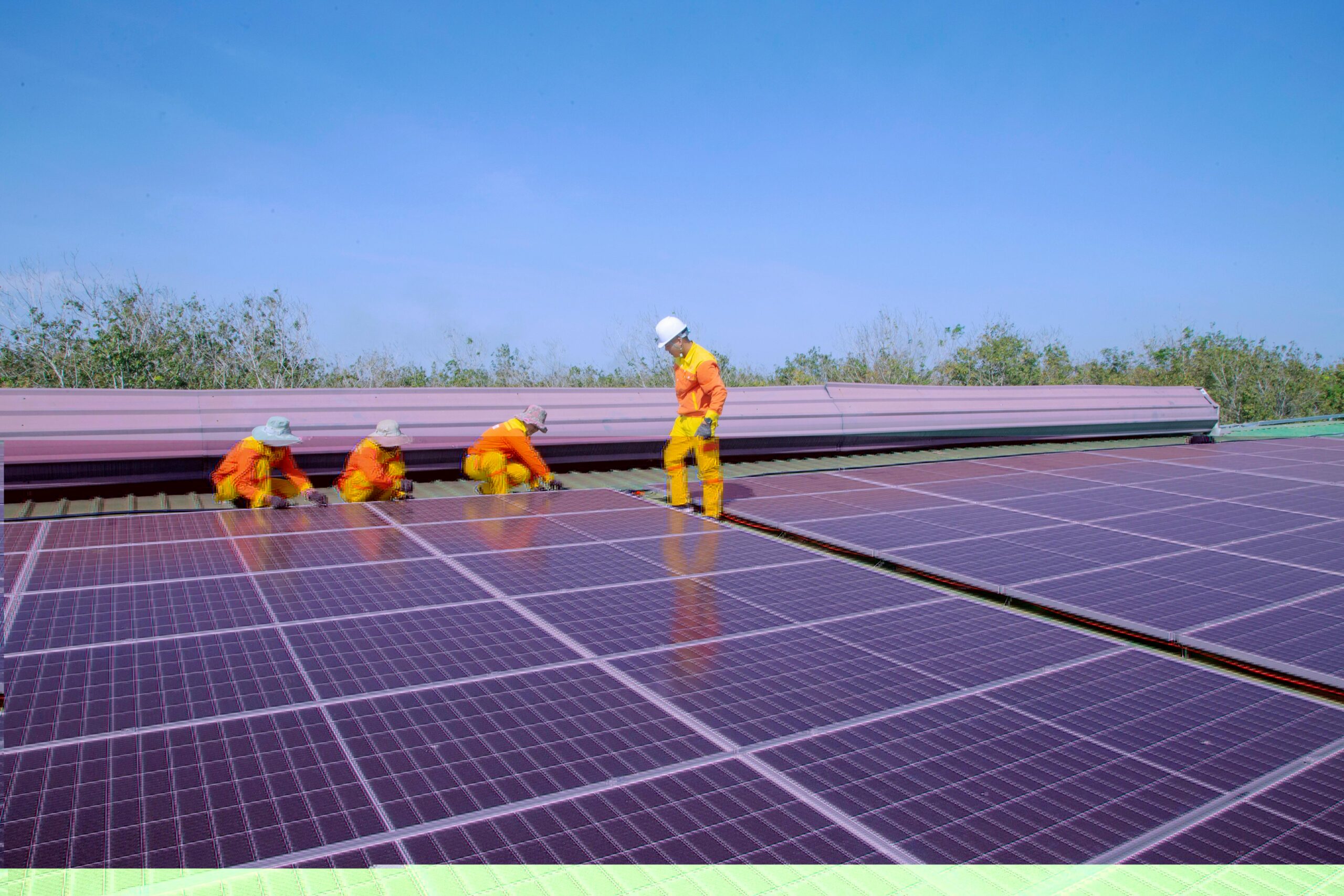
First Net-Zero Academy to train 100,000 workers in the EU solar photovoltaic value chain
To promote a more circular economy and a net-zero value chain, the Commission has launched the European Solar Academy, which aims to train 100,000 workers in the solar sector over the years to address the unemployment gap. It seeks to reduce dependency on non-renewable resources, enhance biodiversity, and promote innovation in bio-based products and services. It also aligns with the European Green Deal, emphasizing collaboration among stakeholders, research investments, and market development. Thierry Breton, Commissioner for Internal Market notes on the importance of training a workforce in sustainability to “meet our objective to manufacture by 2030 at least 40% of our net-zero technology needs”.
Enhancement of Trade Screening Processes
In addition, to counteract economic threats, the EU is strengthening its financial, energy and telecommunications markets. Enrico Letta, the Former Italian prime minister, told the Financial Times that “the problem is that in this new world, we are too small. And if we don’t integrate, we will decline”. Therefore, Europe is seeking new measures to not fall behind with the rest of the world. One of these measures includes the vetting of foreign investments by ensuring that all Member States have a screening mechanism in place. The goal is to prevent the acquisition of sensitive technologies and assets by potentially hostile entities, thus safeguarding national security and economic stability.
Regulations on Exports of Dual-Use Goods
The European Commission highlights that dual-use goods—items that can be utilized for both civilian and military applications (such as advanced electronics), constitute approximately 20% of total EU exports. As a result, the Commission proposes to introduce uniform EU controls on those items that were not adopted by the multilateral export control regimes due to the blockage by certain members. This initiative aims to prevent the misuse of such goods by malign actors, ensuring that exports do not contribute to the military capabilities of countries posing a security threat.
“We must improve our understanding and coordination in tackling these shared challenges so we can better protect ourselves, make investments safer and control the export of sensitive products to avoid them getting into the wrong hands.”
Valdis Dombrovskis, Executive Vice-President and Commissioner for Trade
Increased Support for Research and Development in Strategic Technologies
Recognizing the importance of technological leadership, the EU is ramping up support in the research sector, allocating €95.5 billion for Horizon Europe, its flagship R&D program. This includes funding for innovation in areas such as artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and quantum computing. This measure is supported by Iliana Ivanova, Commissioner for Innovation, Research, Culture, Education and Youth, where she “invites public authorities, civil society, industry and academia across Europe to have their say on options for better support to research”. This action follows the principle “as open as possible, as closed as necessary”, maintaining its competitive edge and reduced dependency on external technological sources.
Similar Posts
Comparison with other World Powers
The EU’s initiatives can be compared with China and the USA who have also implemented strong economic security measures. The USA, for example, has worked on the Committee of Foreign Investment in the United States (CFIUS) to screen foreign investments and the Export Control Reform Act (ECRA) to regulate dual-use exports. These frameworks aim to protect critical technologies and infrastructure from foreign exploitation.
On the other hand, China’s economic security strategy is tightly interwoven with its state-centric economic model, having the country’s Foreign Investment Law reflect its efforts to regulate foreign investment. Additionally, China’s “Made in China 2025” initiative underscores its commitment to achieve technological self-sufficiency and global leadership in high-tech industries.
In a nutshell
The European Commission’s new measures are poised to have significant impacts both within the EU and globally. This include the protection and freedom of its citizens, the development of a strong economy, sustainability, and the enforcement of a single market. However, successful implementation will depend on balancing these objectives with the principles of open trade and cooperation, ensuring inclusivity, and fostering innovation and competitiveness across the Union.