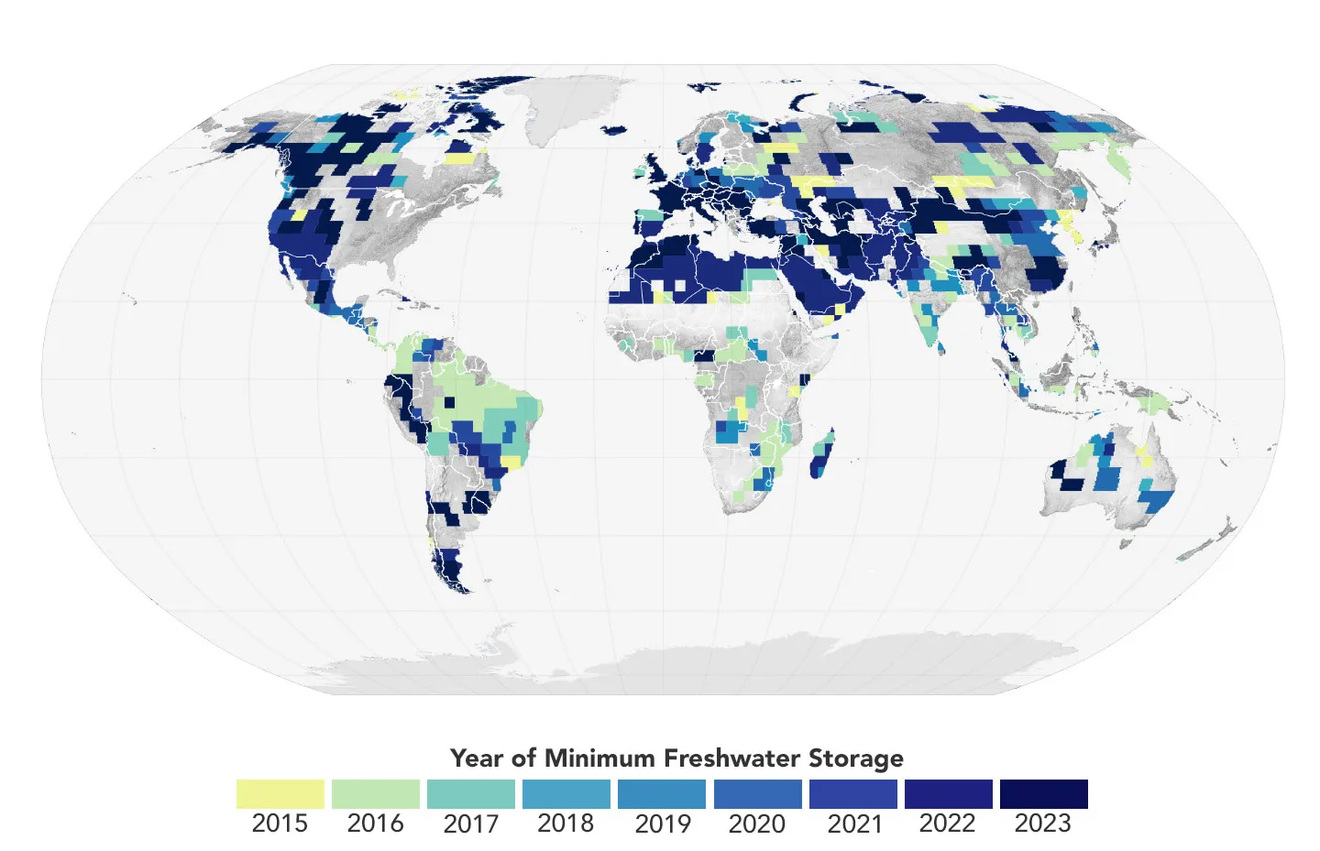
Earth’s freshwater reserves have plummeted since May 2014, marking what scientists believe could be a permanent shift toward a drier planet. NASA-German satellite observations reveal a stark reality: our planet has lost 290 cubic miles of freshwater – equivalent to 2.5 Lake Eries vanishing from the Earth’s surface and underground aquifers.
The Hard Numbers Behind Water Loss
“From 2015 through 2023, satellite measurements showed that the average amount of freshwater stored on land was 1,200 cubic kilometers lower than the average levels from 2002 through 2014,” reports Matthew Rodell, hydrologist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.
The GRACE (Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment) satellites and their successor GRACE-FO have measured these changes through gravitational fluctuations, providing monthly snapshots of Earth’s water mass distribution.
Global Warming’s Water Vapor Trap
NASA Goddard meteorologist Michael Bosilovich explains the technical mechanism: “Warming temperatures increase both the evaporation of water from the surface to the atmosphere, and the water-holding capacity of the atmosphere, increasing the frequency and intensity of drought conditions.”
This creates a troubling cycle:
- Higher temperatures force more water vapor into the atmosphere.
- Soil becomes compact during extended dry periods.
- When intense rains finally arrive, the hardened ground cannot absorb water effectively.
- Runoff increases while groundwater recharge decreases.
Regional Impact and El Niño Connection
The decline began with severe drought in northern and central Brazil, cascading across continents:
- Australasia
- South America
- North America
- Europe
- Africa
The 2014-2016 El Niño, one of the strongest since 1950, disrupted global weather patterns. However, unlike previous cycles, water levels failed to recover after El Niño subsided.
Scientific Uncertainty and Future Projections
Virginia Tech hydrologist Susanna Werth offers a cautionary note: “There are uncertainties in climate predictions. Measurements and models always come with errors.”
Yet the correlation between water loss and rising temperatures cannot be ignored. The nine warmest years in modern temperature records coincide with this unprecedented freshwater decline.
More Stories
Human Cost and UN Warnings
The 2024 UN water stress report outlines cascading effects:
- Agricultural strain
- Urban water scarcity
- Increased groundwater pumping
- Potential famine risk
- Water-related conflicts
- Public health threats from contaminated sources
Satellite Technology’s Role
The GRACE mission, a collaboration between NASA and the German Aerospace Center, has revolutionized water monitoring:
- Original GRACE satellites (2002-2017)
- GRACE-FO continuation (2018-present)
- Monthly gravity measurements
- Global coverage
- Underground water detection capability
Looking Ahead: A Drier Future?
Since 2015, GRACE has recorded 13 of the 30 most intense droughts in its observational history. Rodell suggests this pattern “could be a harbinger of what’s to come.”
The data presents clear evidence of a planetary-scale shift in freshwater distribution, demanding immediate attention to water conservation and management strategies.