A contract has been signed between Luc Piquet, ClearSpace CEO and co-founder, and Stéphane Israël, Arianespace CEO, for the launch of the ClearSpace 1 mission in 2026. A launch contract for ClearSpace 1, an active debris removal mission targeting objects over 100 kg, has been finalized by ClearSpace and Arianespace. Scheduled for the second half of 2026, the launch will utilize the new European light launcher Vega C.T.
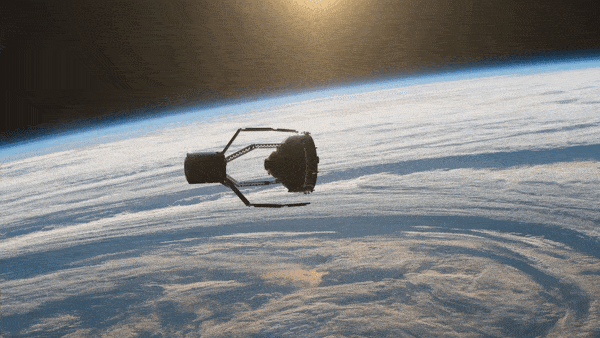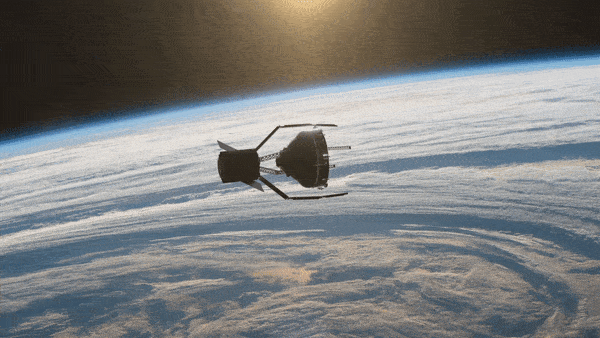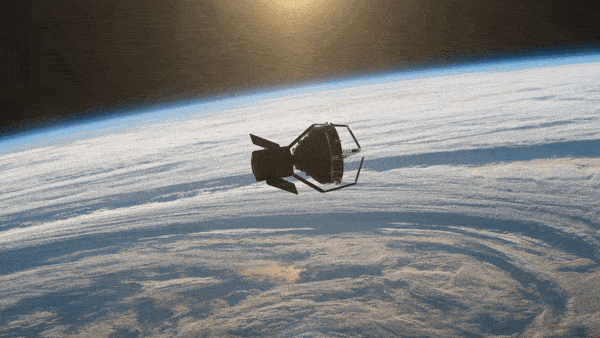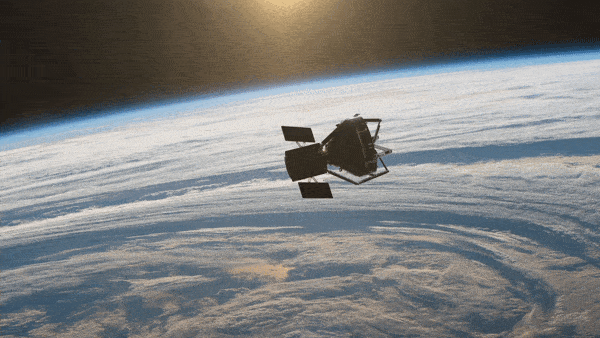
The spacecraft will be released into a sun-synchronous drift orbit for commissioning and critical tests. The aim of ClearSpace-1 is to capture and deorbit a derelict space debris object, the upper part of a Vespa, left in a disposal orbit in 2013. Providing an opportunity to demonstrate the spacecraft’s technologies and quartet of robotic arms, the target space debris object has a mass similar to that of a small satellite.
A $103 million deal in 2020 for the cleanup mission was secured by ClearSpace in partnership with the European Space Agency (ESA). Operating from a spaceport in French Guiana, Arianespace has been chosen as the launch service provider for ClearSpace-1.
The objective of the mission is to recover a portion of the Vega Secondary Payload Adapter (Vespa) that has been orbiting Earth since 2013. With success opening doors for more challenging missions, ClearSpace will test its unique robotic arm designed to grab space junk.
The Earth has been surrounded by space debris since the dawn of space exploration in the last century. Along with approximately 6,500 operational satellites, over 34,000 pieces of space debris larger than 10 centimeters currently exist. By the end of the decade, the number of operational satellites is expected to exceed 27,000.
In order to preserve the benefits of space for humanity and life on Earth, Stéphane Israël emphasizes the need for innovative solutions. Addressing the issue of space debris accumulation, the ClearSpace mission represents a turning point in the space industry.
The ESA selected ClearSpace in 2019 to lead the first mission to remove an ESA-owned item from orbit. Part of ESA‘s Space Safety Program, the mission aims to establish a new market for in-orbit servicing and debris removal.
Similar Posts
ESA has identified over 30,000 pieces of space debris as of April 2022, posing risks to operational spacecraft. Potentially exceeding 1 million objects larger than 1 centimeter, an increasing number of unidentified objects are allowed to be detected by improving technology.
The necessity of finding innovative solutions to preserve the benefits of space for humanity is reiterated by Arianespace CEO Stéphane Israël. The way for a new market focused on in-orbit servicing and debris removal is paved by ClearSpace, supported by ESA’s Space Safety Program. The urgency of finding solutions to the growing problem of space debris accumulation is highlighted by ClearSpace CEO. Luc Piguet.