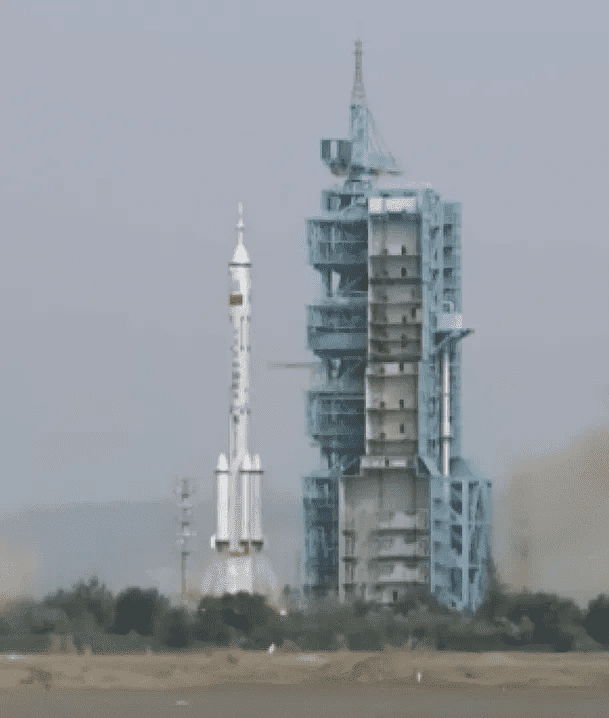
While the aim of the US is to impede Beijing’s advancement in industries like semiconductors, the Shenzhou 16 mission of China, launched from the Gobi Desert, highlights the country’s rapid progress in its space program. Carrying three astronauts, the Long March-2F rocket took off from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, marking China’s 11th crewed mission and closing the gap in the space race with the US. Significant milestones, including being the first nation to land on the far side of the moon in 2019 and successfully landing a rover on Mars in 2021, have been achieved by China.
Owing to US objections to Chinese involvement in the International Space Station, China operates its own space station. Lin Xiqiang, an official from the China Manned Space Agency, has stated that the country plans to send Chinese astronauts to the moon by 2030. Foreign reporters were allowed to visit the military-controlled launch center, thus providing access rarely granted and underscoring the role of the People’s Liberation Army in the space program prior to the launch.
An independent scholar on space policy, Namrata Goswami, noted that China’s operational success in space allows them to commercialize and gain visibility not only in the US but also among nations participating in the Belt and Road initiative. Three Chinese astronauts are a part of the latest Shenzhou mission, rendezvousing with others aboard the Tianlong space station as part of the government’s plan for continuous occupation and scientific exploration.
Similar Posts
In a letter to a UN symposium, President Xi Jinping emphasized China’s willingness to collaborate and use outer space for peaceful purposes and the benefit of all countries. The US-led camp continues to pursue its own space diplomacy, including initiatives like the Artemis Accords, while China has made progress in its space program. The complex dynamics and competition in the space domain are reflected in the decision of the European Space Agency not to plan a mission with China.
The space program of China provides an opportunity for global collaboration and cooperation in exploring the universe and advancing space technology for the benefit of all nations. A key element in President Xi Jinping’s strategy to improve the country’s global image following criticisms of its COVID Zero policy is China’s space program. The achievements of China in space and its ambition to send astronauts to the moon contribute to the country’s growing status as a major player in the space race.
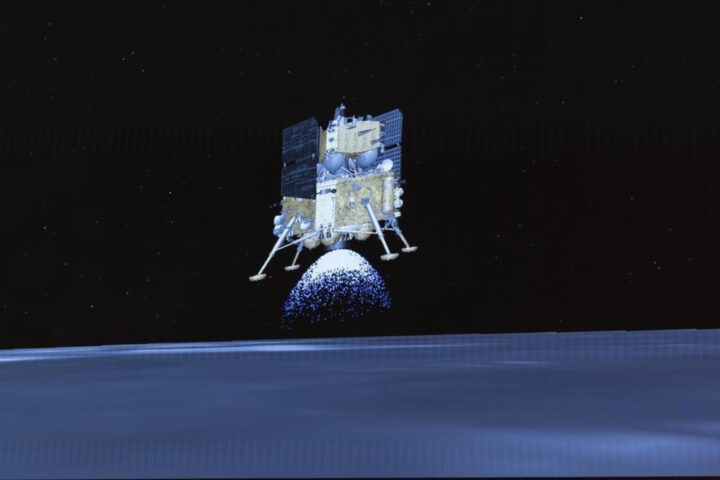














![This image taken from video animation at Beijing Aerospace Control Center (BACC) on June 2, 2024 shows the lander-ascender combination of Chang'e-6 probe landing on the far side of the moon. [Photo/Xinhua]](https://www.karmactive.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/spp.jpeg)