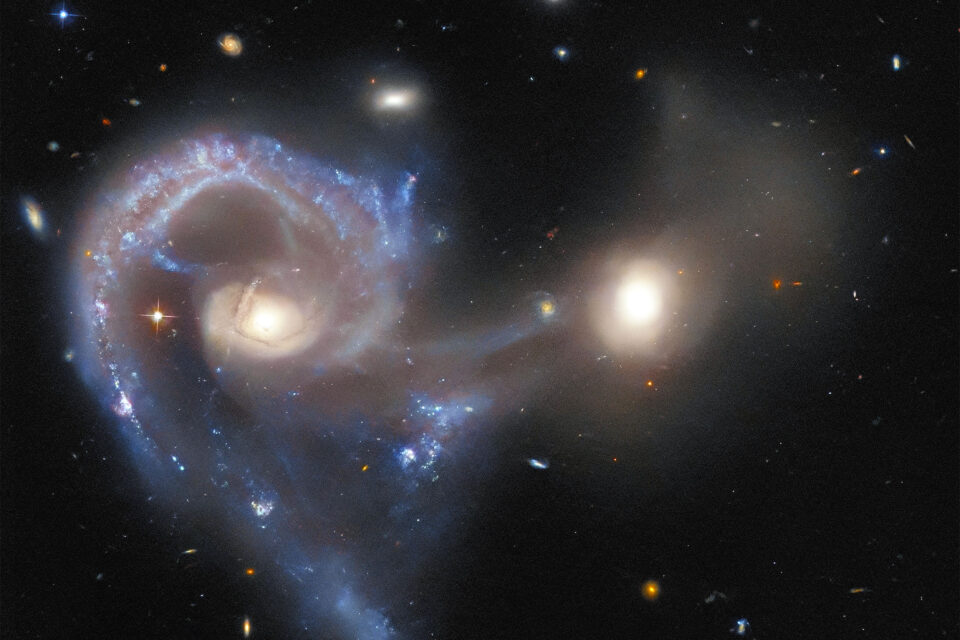
The Hubble Space Telescope recently unveiled a captivating image of Arp 107, a pair of colliding galaxies located approximately 465 million light-years away in the constellation of Leo Minor. These celestial entities are on a trajectory to merge into a singular, massive galaxy, mirroring the anticipated future of our Milky Way and Andromeda. “Arp 107 is one of 338 galaxies catalogued by American Astronomer Halton Arp in the 1960s, focusing on the universe’s most unique galactic formations,” the report highlighted.
The observation of Arp 107 was part of a strategic initiative to maximize Hubble’s observational time, filling in gaps between its planned schedules. This program not only advances scientific understanding but also gifts the public with awe-inspiring images of galaxies that defy conventional categorization. The left side of the Hubble image showcases a Seyfert galaxy, distinguished by its supermassive black hole core. This black hole’s intense gravitational pull causes surrounding gas, dust, and stars to emit light across the electromagnetic spectrum, making it exceptionally luminous.
The Seyfert galaxy’s core is home to an active galactic nucleus, often referred to as a “bright black hole.” A delicate bridge of material, evidence of their impending merger, connects the two galaxies. The backdrop of the Hubble image is adorned with a myriad of distant galaxies, some of which are also interacting, offering a broader perspective on the universe’s dynamic nature. Foreground stars in the image display cross-shaped diffraction spikes, a signature effect caused by light’s interaction with Hubble’s internal support structure.
NASA described a “magnificent bridge of gas and dust” suspended between the two galaxies, emphasizing the grandeur of this cosmic connection. The Hubble Space Telescope, a collaborative mission between NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA), has a primary focus on exploring the lesser-known members of the Arp 107 system. The Seyfert Galaxy in Arp 107 is characterized by a large spiral arm, illuminated by budding stars, which owe their luminance to materials from the smaller galaxy it’s merging with. “The radiation from the active galactic nucleus can potentially overshadow the collective luminance of every single star within the galaxy,” the report detailed.
Similar Posts
In stark contrast to the Seyfert Galaxy, the smaller galaxy, although possessing a bright core, has fainter spiral arms, hinting at its ongoing absorption. ESA officials recently commented, “Despite the active core’s immense brightness, radiation from the entire Seyfert galaxy can be observed, with the spiraling patterns of the whole galaxy clearly visible.” Both galaxies are integral members of the ‘Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies,’ a compilation crafted in 1966 by Halton Arp.
The recent Hubble image not only mesmerizes with its beauty but also deepens our comprehension of the cosmos and the evolutionary processes of celestial bodies. As these galaxies edge closer to their merger, the scientific community eagerly awaits the revelations this union might bring. A faint gas “bridge” connects the two colliding galaxies, further captured in the Hubble Space Telescope’s recent photo. The Arp 107 system’s larger galaxy, known as a Seyfert galaxy, houses an active galactic nucleus, a phenomenon associated with supermassive black holes.
ESA officials emphasized the visibility of the entire Seyfert galaxy, from its radiant core to its spiraling arms. The smaller galaxy, while having a luminous core, is gradually being integrated into the Seyfert galaxy, as evidenced by its fainter arms. Arp 107 is part of the Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies, a collection initiated in 1966 by Halton Arp, aiming to document the universe’s most unusual galactic structures. The recent Hubble image was captured to shed light on the lesser-studied members of the Arp catalog, enriching our understanding of these cosmic wonders. “Our intention with this observing programme is to offer the public images of these spectacular galaxies that challenge easy definitions,” stated ESA, emphasizing the blend of science and artistry in their endeavors.