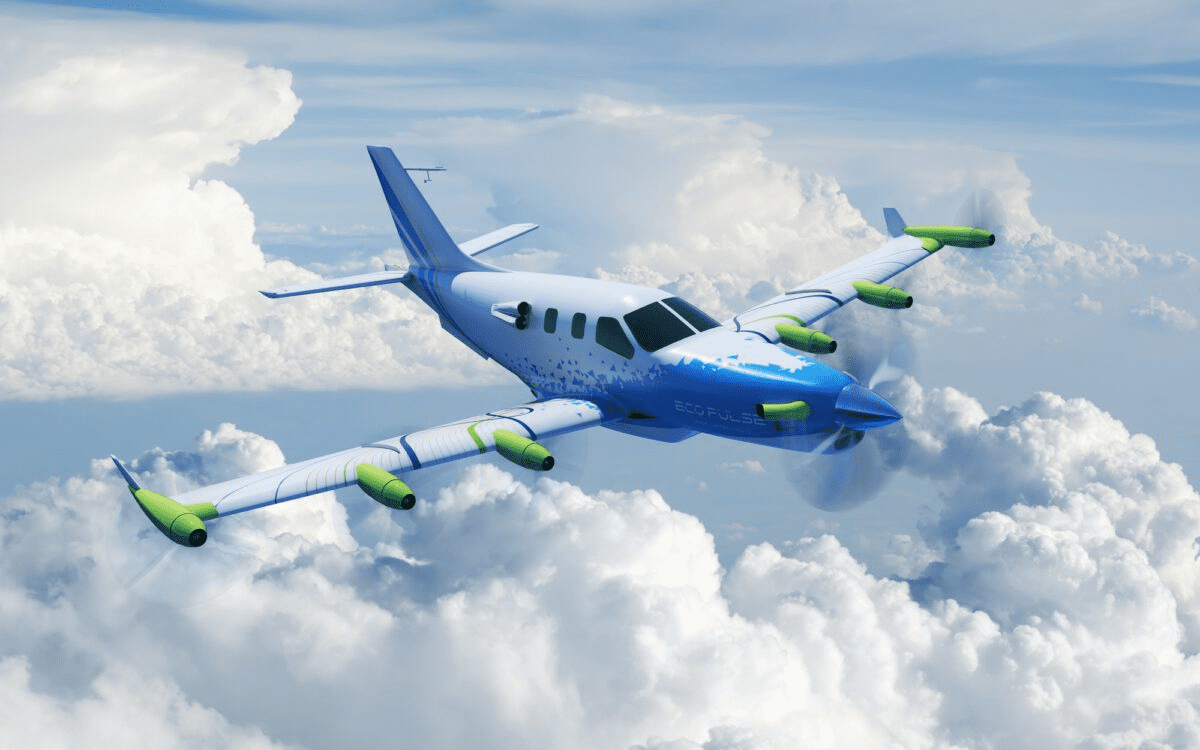
EcoPulse, the wing-mounted, hybrid-electric distributed propulsion aircraft demonstrator jointly developed by Daher, Safran, and Airbus, has made its much-anticipated debut at the 2023 Paris Air Show. This revolutionary aircraft, based on Daher’s TBM 900-series airplanes, represents a significant step forward in the quest for aviation decarbonization and operational efficiency.
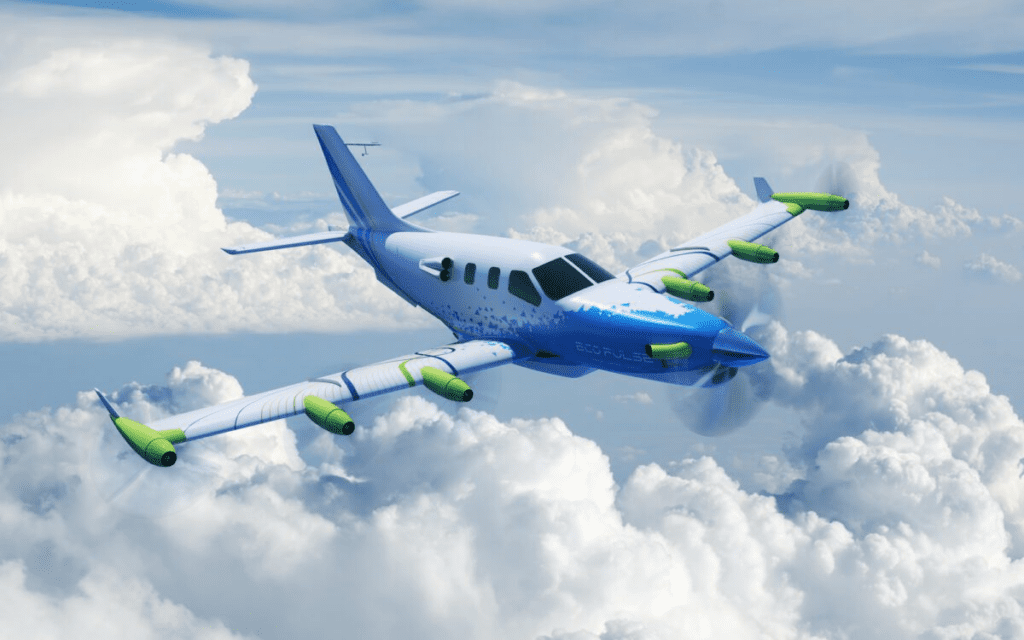

The primary objective of the EcoPulse project is to evaluate the numerous benefits of integrating hybrid-electric distributed propulsion, with a particular emphasis on reducing CO2 emissions and minimizing noise levels. By adopting this disruptive propulsion architecture, the aircraft can rely on a single, independent electrical power source to supply multiple engines distributed throughout its structure.
The demonstrator boasts six integrated electric thrusters, also known as e-Propellers, positioned strategically along the wings. These cutting-edge thrusters are supplied by Safran, a key partner in this venture. The EcoPulse propulsion system encompasses two power sources: a turbogenerator, an electric generator driven by a gas turbine, and a battery pack. Both of these units are supplied by Safran and Airbus, respectively. At the heart of this innovative architecture lies the Power Distribution and Rectifier Unit, responsible for safeguarding the high-voltage network and efficiently distributing the available electrical power. Furthermore, Safran provides the high-voltage power harnesses, which play a crucial role in the aircraft’s power distribution.
Similar Post
The path to the public debut of the EcoPulse demonstrator has been marked by significant achievements and milestones. Ground and flight tests conducted in 2023 successfully validated the aircraft’s aerodynamics and system configuration. Notably, the demonstrator has already accumulated approximately 27 hours of flight time, albeit with the electric propellers in a feathered state. Later this year, the next phase of flight tests for the hybrid-electric powertrain will commence. These tests will further refine and optimize the aircraft’s performance.
The French Civil Aviation Authority and the French Civil Aviation Research Council (CORAC) have provided their valuable support and co-funding. The collaboration has garnered recognition as one of the major initiatives in France dedicated to advancing aviation decarbonization.
Looking ahead, the EcoPulse project envisions the development of a hybrid aircraft that can be introduced to the market by the end of 2027. The goal is to offer a sustainable solution that contributes to reducing emissions and enhancing overall energy efficiency in the aerospace industry.
In parallel with EcoPulse, Airbus is actively engaged in other research projects focused on wing technologies, including Wing of Tomorrow and Extra Performance Wing. While these projects share commonalities with HERWINGT, they target different aircraft segments and flight conditions. Through the utilization of shared materials and integrated systems, these initiatives collectively push the boundaries of innovation and propel the aerospace industry toward a more sustainable future. With its pioneering approach and commitment to sustainable aviation, EcoPulse will inspire other industry players to adopt greener technology for the next genera