The pristine, frozen continent of Antarctica is facing the brunt of climate change as the situation inches towards an alarming point. The recent photographs showcase a worrisome loss in sea ice, which has grave consequences for the global climate as well as causing damage to the arctic ecology. As reported by the British Antarctic Survey (BAS), the Thwaites glacier is swiftly melting, which could result in a three-meter rise in sea levels within a century. There is an urgent need for scientific collaboration to gain an in-depth understanding of the Antarctic’s impact on the planet in the face of these dramatic changes.
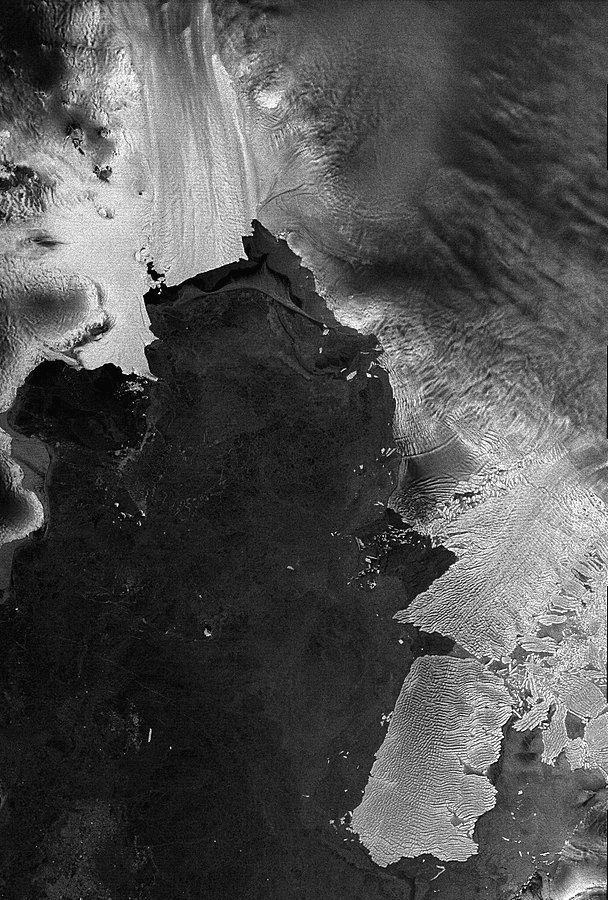

Unprecedented Sea Loss
In contrast to the previously observed stability across the region, satellite data from late 2022 to early 2023 depicts an unprecedented drop in sea ice around Antarctica. This reduction continued even during the harshest winter months, raising concerns about the continent reaching a tipping point. The mass of sea ice in Antarctica was significantly below long-term averages, as per the observations made in mid-June 2023.
Global Implications of Antarctic Changes
The repercussions of Antarctica’s changing climate extend beyond its borders. Warming polar seas affect weather patterns worldwide and accelerate the melting of Antarctic glaciers, contributing to global sea level rise. The polar regions are at the forefront of climate change and witness its impacts before other regions. Sea ice plays a critical role in driving deep water currents, and its loss can have profound consequences on a global scale.
Threats to Ecosystems and Species
The diminishing sea ice poses a threat to numerous Antarctic species that rely on it for breeding and survival. Iconic species like emperor penguins have already suffered due to changes in sea ice patterns, resulting in the loss of multiple generations of chicks. Additionally, the retreat of coastal sea ice exposes vulnerable glaciers, such as the Thwaites glacier, to warming ocean waters. If the current trend continues, the collapse of the Thwaites Ice Shelf, a protective barrier for the continental glacier, becomes more likely.
The Doomsday Glacier and Rising Sea Levels
The Thwaites Glacier, dubbed the “Doomsday Glacier,” is a critical concern due to its vulnerability and potential impact on global sea levels. It currently contributes 4% to the global sea level rise, and complete melting could raise sea levels by 65 centimeters. Recent studies indicate that the Thwaites Ice Shelf might collapse entirely by the early 2030s, an event that could accelerate if sea ice continues to vanish. Despite all the signals, hope to mitigate the situation remains. Evidently, immediate action is needed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Similar Post
The Race to Understand and Address Climate Change
Scientists at the BAS are racing against time to comprehend the composition of the bedrock beneath the Thwaites glacier, which could influence the speed of its collapse. However, the rate of change and the complexity of Antarctic climate necessitate a shift in scientific approaches. Collaboration and integration of research across various disciplines are crucial to gaining a comprehensive understanding of the Antarctic’s role in shaping the planet’s climate.
The Urgent Need for Action
Antarctica’s drastic transformation indicates that the world has entered a new phase of planetary climate, unprecedented in the last 800,000 years. The BAS aims to extend its knowledge further, but the Earth’s warm past provides limited insights. Addressing the challenges posed by climate change requires immediate action to curb carbon emissions and protect the fragile Antarctic ecosystem. The consequences of tipping points remain uncertain, emphasizing the urgency to halt further deterioration.
Conclusion: Antarctica’s rapidly changing climate presents a dire situation with global ramifications. The decline in sea ice, the vulnerability of key ice sheets like the Thwaites glacier, and the potential for significant sea level rise demand immediate attention.