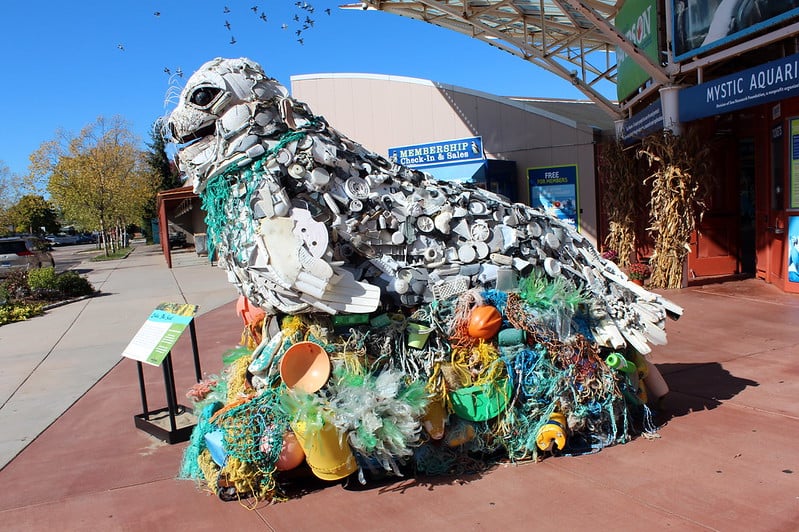
The world’s nations gather in Busan, South Korea from November 25 to December 1, 2024, for what could be the final round of negotiations on a legally binding treaty to address plastic pollution. With 196 countries participating, the fifth session of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC-5) faces the complex task of resolving deep divisions over plastic production controls.
Production Curbs: The Core Conflict
The United States shifted its stance on plastic production regulation between INC-4 in April and INC-5, potentially altering the treaty’s trajectory. After initially focusing on recycling and reuse, the U.S. now acknowledges the need to regulate plastics throughout their lifecycle, including production. This change puts pressure on other major producers like China, Russia, India, and Saudi Arabia, who have opposed production controls.
“With today’s shift in position to support plastic production caps and regulate chemicals via the UN Plastics Agreement, the White House has signaled it is willing to betray U.S. manufacturing and the hundreds of thousands of jobs it supports,” stated the American Chemistry Council, representing petroleum producers.
Current State of Crisis
The numbers tell a stark story. Global plastic production has surged over 200-fold since 1950, reaching over 400 million tonnes annually. Half consists of single-use plastics. As of 2015, only 9% of all plastic waste ever produced had been dealt with. With 19 million tonnes of plastic leaking into the environment each year, contamination reaches from the Mariana Trench to Antarctic snow.
Of 16,000 known chemicals in everyday plastics, 4,200 pose risks to human health or the environment. Plastic particles have infiltrated human food, blood, placentas, and breastmilk.
Key Challenges in Busan
The draft treaty text remains contested, with over 3,000 bracketed sections indicating disagreement. Major points of contention include:
- Chemical bans in plastic products
- Funding mechanisms for treaty implementation
- Production limits and controls
- Waste management strategies
- Decision-making procedures
“This treaty is going to be assessed on the extent to which the world begins to limit plastic production and consumption to sustainable levels,” said Dennis Clare, legal adviser for the Federated States of Micronesia.
Bridge to Busan Initiative
Forty nations and the European Union have signed the Bridge to Busan declaration, pushing for “sustainable levels of production.” However, the U.S. has not yet joined, despite its recent policy shift.
“We need to know more,” said WWF vice president Erin Simon about the U.S. position change, while suggesting it may isolate nations opposing a strong international agreement.
Industry Response and Economic Implications
Petrochemicals drive oil demand growth, making production cuts economically sensitive for fossil fuel-producing nations. Some countries appear to be accelerating petrochemical plant construction ahead of potential restrictions.
“Asia is the key region for growth of the petrochemicals industry… Korea is also massively investing in the petrochemicals build-out,” explained Delphine Levi Alvares from the Center for International Environmental Law.
More Stories
Environmental Justice
Hundreds have marched in Busan demanding reduced plastic production. The Break Free from Plastic Movement connects plastic pollution to climate change, biodiversity loss, and toxic pollution. Indigenous rights groups and waste pickers bring direct experience of plastic pollution impacts to the negotiations.
Looking Ahead
With six days to reach agreement, INC-5 Chair Luis Vayas Valdivieso has prepared a streamlined text version to prioritize discussions. If successful, the treaty could open for ratification by mid-2025. Failure to reach agreement could extend negotiations into 2025.
“It will be extremely challenging and take many years to add something on production retrospectively if there aren’t the requisite hooks in the treaty text,” warned Christina Dixon, ocean campaign leader at the Environmental Investigation Agency.
The outcome in Busan will determine whether the world can effectively address plastic pollution through coordinated global action or remain caught in a cycle of increasing production and environmental damage.