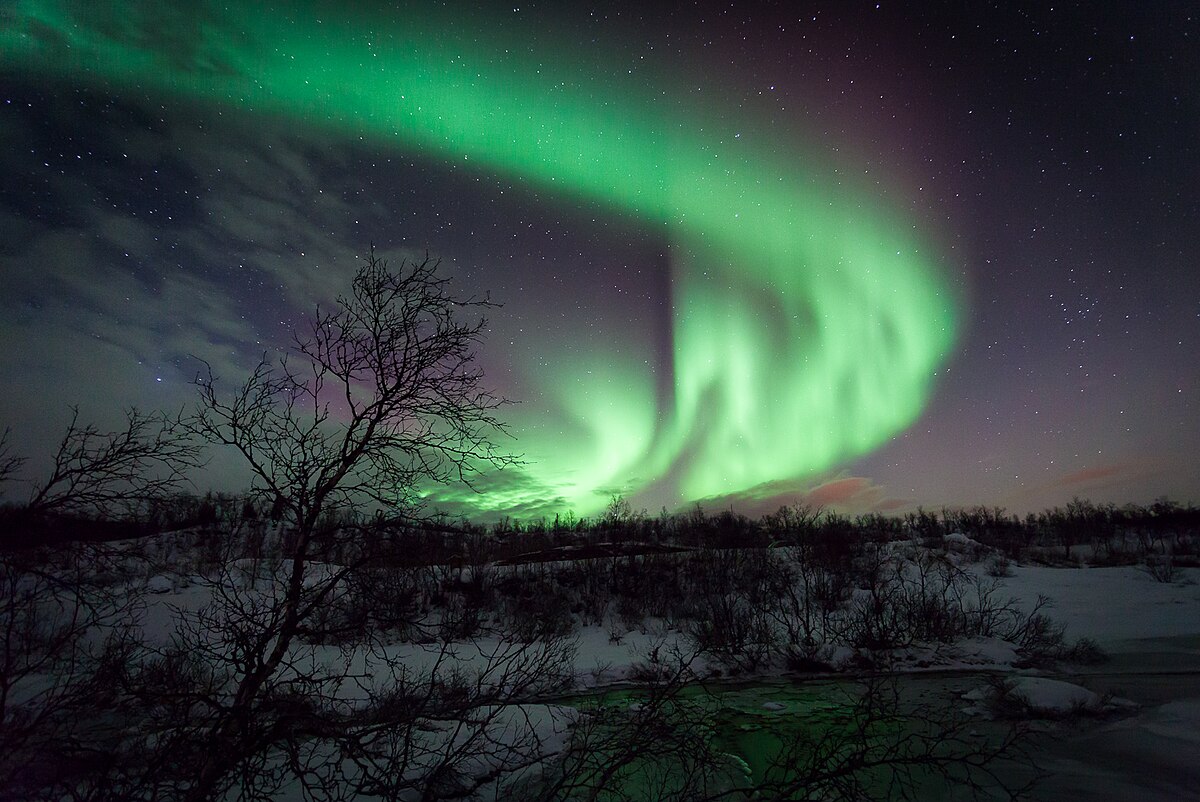
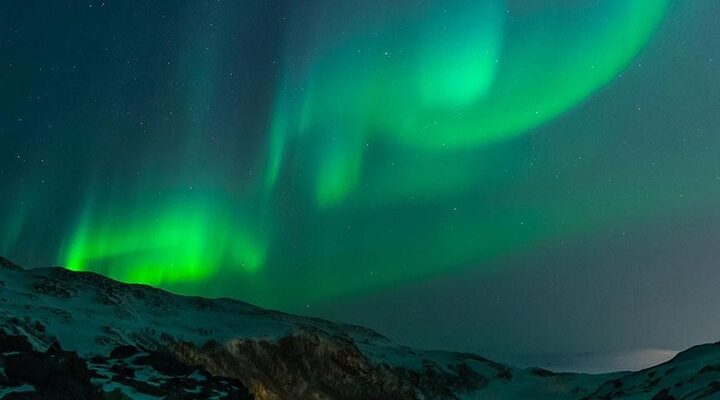
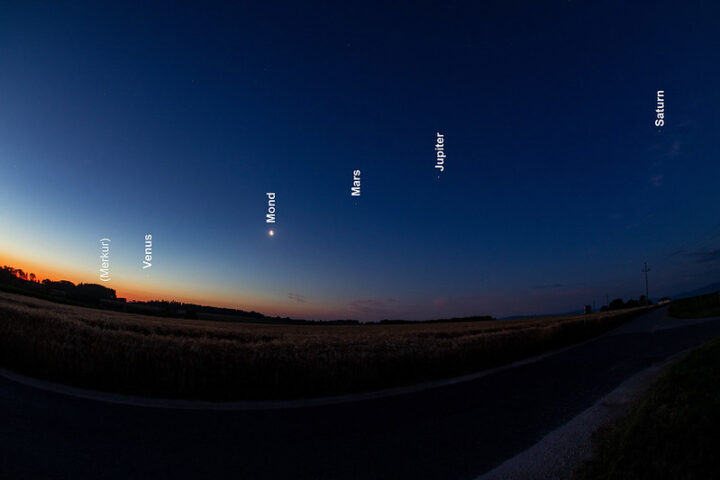
Recent increases in solar activity have led to a surge in northern lights sightings, captivating skywatchers across the northern latitudes. The Sun’s current active phase is driving more frequent and intense auroral displays, offering unprecedented opportunities for viewing this mesmerizing natural phenomenon.
Causes and Mechanics of Auroras
Auroras, known as the northern lights (aurora borealis) in the Northern Hemisphere and southern lights (aurora australis) in the Southern Hemisphere, occur when charged particles from the Sun collide with Earth’s atmosphere. These particles, primarily electrons and protons, are ejected from the Sun during solar events such as coronal mass ejections and solar flares.
As these charged particles approach Earth, they interact with our planet’s magnetic field. The field guides the particles towards the polar regions, where they collide with atmospheric gases, primarily oxygen and nitrogen. These collisions excite the gas molecules, causing them to release energy in the form of light – creating the colorful, shimmering curtains of the aurora.
NOAA Forecasts: Predicting Auroral Activity
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) provides crucial forecasting tools for aurora enthusiasts. Their Space Weather Prediction Center offers several resources:
- Aurora Viewline: This experimental forecast shows the predicted southern extent of aurora visibility for the current and following nights.
- 30-Minute Aurora Forecast: Provides short-term predictions of auroral activity, allowing viewers to plan their observations more precisely.
- Aurora Dashboard: An experimental tool offering a comprehensive overview of current auroral conditions and predictions.
These tools utilize data from solar observations and models of Earth’s magnetosphere to predict the intensity and location of auroral displays.
Prime Viewing Locations in the United States
For the next 1-2 nights, NOAA forecasts suggest optimal viewing conditions in:
- Alaska
- Northern Pacific Northwest (Washington, Oregon, Idaho)
- Northern Midwest/Great Lakes region (Michigan, Minnesota, Wisconsin)
Generally, locations above the 45th parallel north latitude in the continental United States offer the best chances for aurora sightings.
Timing Your Aurora Experience
Auroral activity typically peaks during the overnight hours. The most favourable viewing times usually fall between 10 PM and 2 AM local time when the sky is at its darkest. However, intense auroral events can sometimes be visible earlier in the evening or later in the morning.
Tips for Successful Aurora Viewing
- Monitor NOAA forecasts regularly in the days leading up to potential aurora events.
- Choose a location away from city lights with an unobstructed view of the northern horizon.
- Allow time for your eyes to adjust to the darkness – typically 20-30 minutes.
- Dress warmly and be prepared to spend several hours outdoors.
- Bring a red-light flashlight to preserve your night vision.
- Be patient, as auroral intensity and visibility can fluctuate rapidly throughout the night.
Similar Posts
Global Aurora Hotspots
While the current focus is on U.S. locations, several global destinations are renowned for northern lights viewing:
- Fairbanks, Alaska, USA
- Yellowknife, Northwest Territories, Canada
- Tromsø, Norway
- Reykjavik, Iceland
- Rovaniemi, Finnish Lapland
These locations offer a combination of high latitude, clear skies, and infrastructure to support aurora tourism.
The Science Behind the Spectacle
NASA explains: We’re entering a period of increased solar activity, part of the approximately 11-year solar cycle. This heightened activity leads to more frequent and intense coronal mass ejections and solar flares, which in turn can trigger stronger auroral displays.
Recent research has enhanced our understanding of auroral physics. A study revealed new insights into the formation of pulsating auroras, a specific type of aurora that appears as patches of light turning on and off in the night sky.
Aurora Tourism: Economic Impact and Cultural Significance
The global northern lights tourism market size was estimated at USD 834.5 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.8% from 2024 to 2030. The Northern Lights, or Aurora Borealis, have long enchanted and captivated people worldwide.
This growth has significant implications for local economies in aurora-viewing regions. In Finnish Lapland, for example, aurora tourism accounts for approximately 10% of the region’s annual tourism revenue, according to Visit Finland.
However, the influx of tourists also raises concerns about environmental impact and cultural preservation. Many viewing locations are in ecologically sensitive areas or regions with indigenous populations. Sustainable tourism practices are crucial to balance economic benefits with environmental and cultural preservation.
Capturing the Aurora: Photography and Social Media
Advances in digital camera technology have revolutionized aurora photography. Modern DSLR and mirrorless cameras, capable of high ISO settings and long exposures, allow amateur photographers to capture stunning images of the northern lights.
Social media platforms have played a significant role in popularizing aurora viewing and photography. Instagram alone hosts approximately 3 million posts tagged #northernlights, showcasing the global fascination with this phenomenon.
As interest in the northern lights continues to grow, driven by increased solar activity and improved forecasting capabilities, more people than ever have the opportunity to witness this awe-inspiring natural light show. Whether viewed as a scientific marvel, a tourism draw, or simply a beautiful display of nature’s wonders, the aurora remains a captivating spectacle that connects us to the vast and dynamic interactions between our planet and the Sun.